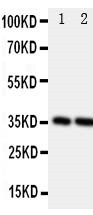
Anti-Podoplanin/gp36 Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q64294 |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Reactivity | Mouse, Rat |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Format | Lyophilized |
| Description | Rabbit IgG polyclonal antibody for Podoplanin(PDPN) detection. Tested with WB in Mouse;Rat. |
| Reconstitution | Add 0.2ml of distilled water will yield a concentration of 500ug/ml. |
| Gene ID | 54320 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Podoplanin, E11 antigen epitope, Glycoprotein 38, Gp38, OTS-8, RTI140, T1-alpha, T1A, Type I cell 40 kDa protein, Pdpn, Gp38, Ots8 |
| Calculated MW | 17579 MW KDa |
| Application Details | Western blot, 0.1-0.5 µg/ml, Rat, Mouse |
| Subcellular Localization | Membrane ; Single-pass type I membrane protein . Cell projection, lamellipodium membrane ; Single-pass type I membrane protein . Cell projection, filopodium membrane ; Single-pass type I membrane protein . Cell projection, microvillus membrane ; Single-pass type I membrane protein . Cell projection, ruffle membrane ; Single-pass type I membrane protein . Localized to actin-rich microvilli and plasma membrane projections such as filopodia, lamellipodia and ruffles. |
| Tissue Specificity | In adult kidney, expressed on the urinary surface and foot processes of podocytes and in parietal epithelial cells of Bowman's capsule where it is localized to luminal surfaces. In lung, expressed exclusively on luminal surfaces of type I alveolar epithelial cells and pleural mesothelial cells. Not expressed in type II alveolar cells. In bone, expressed in osteocytes and osteoblasts. In spleen, liver, stomach and intestine, expressed in mesoepithelium. Also expressed in thymic epithelial cells, choroid plexus and leptomeninges. . |
| Protein Name | Podoplanin |
| Contents | Each vial contains 5mg BSA, 0.9mg NaCl, 0.2mg Na2HPO4, 0.05mg Thimerosal, 0.05mg NaN3. |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence at the C-terminus of rat Podoplanin/gp36(155-166aa VVMRKISGRFSP), different from the related mouse sequence by one amino acid. |
| Purification | Immunogen affinity purified. |
| Cross Reactivity | No cross reactivity with other proteins |
| Storage | At -20˚C for one year. After r˚Constitution, at 4˚C for one month. It˚Can also be aliquotted and stored frozen at -20˚C for a longer time.Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Name | Pdpn {ECO:0000312|RGD:61819} |
|---|---|
| Function | Mediates effects on cell migration and adhesion through its different partners. During development plays a role in blood and lymphatic vessels separation by binding CLEC1B, triggering CLEC1B activation in platelets and leading to platelet activation and/or aggregation. Interaction with CD9, on the contrary, attenuates platelet aggregation and pulmonary metastasis induced by PDPN. Mediates effects on cell migration and adhesion through its different partners. Through MSN or EZR interaction promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) leading to ERZ phosphorylation and triggering RHOA activation leading to cell migration increase and invasiveness. Interaction with CD44 promotes directional cell migration in epithelial and tumor cells (By similarity). In lymph nodes (LNs), controls fibroblastic reticular cells (FRCs) adhesion to the extracellular matrix (ECM) and contraction of the actomyosin by maintaining ERM proteins (EZR; MSN and RDX) and MYL9 activation through association with unknown transmembrane proteins. Engagement of CLEC1B by PDPN promotes FRCs relaxation by blocking lateral membrane interactions leading to reduction of ERM proteins (EZR; MSN and RDX) and MYL9 activation (By similarity). Through binding with LGALS8 may participate in connection of the lymphatic endothelium to the surrounding extracellular matrix. In keratinocytes, induces changes in cell morphology showing an elongated shape, numerous membrane protrusions, major reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton, increased motility and decreased cell adhesion. Controls invadopodia stability and maturation leading to efficient degradation of the extracellular matrix (ECM) in tumor cells through modulation of RHOC activity in order to activate ROCK1/ROCK2 and LIMK1/LIMK2 and inactivation of CFL1 (By similarity). Required for normal lung cell proliferation and alveolus formation at birth (By similarity). Does not function as a water channel or as a regulator of aquaporin-type water channels (By similarity). Does not have any effect on folic acid or amino acid transport (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Membrane; Single- pass type I membrane protein. Cell projection, lamellipodium membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Cell projection, filopodium membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Cell projection, microvillus membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Cell projection, ruffle membrane; Single-pass type I membrane protein. Membrane raft {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q86YL7}. Apical cell membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q86YL7}. Basolateral cell membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q86YL7}. Cell projection, invadopodium {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q86YL7}. Note=Localized to actin-rich microvilli and plasma membrane projections such as filopodia, lamellipodia and ruffles (PubMed:9327748). Association to the lipid rafts is required for PDPN-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) Colocalizes with CD9 in tetraspanin microdomains. Localized at invadopodium adhesion rings in tumor cell. Association to the lipid rafts is essential for PDPN recruitment to invadopodia and ECM degradation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q86YL7, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9327748} |
| Tissue Location | In adult kidney, expressed on the urinary surface and foot processes of podocytes and in parietal epithelial cells of Bowman's capsule where it is localized to luminal surfaces. In lung, expressed exclusively on luminal surfaces of type I alveolar epithelial cells and pleural mesothelial cells. Not expressed in type II alveolar cells. In bone, expressed in osteocytes and osteoblasts. In spleen, liver, stomach and intestine, expressed in mesoepithelium. Also expressed in thymic epithelial cells, choroid plexus and leptomeninges |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
PDPN(Podoplanin), also called T1A, T1A2, GP36, OTS8 or AGGRUS, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PDPN gene. This gene encodes a type-I integral membrane glycoprotein with diverse distribution in human tissues. The PDPN gene is mapped to chromosome 1 by the International radiation Hybrid mapping consortium. The physiological function of PDPN may be related to its mucin-type character. The specific function of this protein has not been determined but it has been proposed as a marker of lung injury. Immunohistochemical analysis of PDPN in placenta, kidney, lung, and nasal polyps showed expression at the apical plasma membrane of vascular endothelial cells and in alveolar epithelial cells. Overexpression of rat PDPN in human and rodent endothelial cells promoted formation of elongated cell extensions and significantly increased endothelial cell adhesion, migration, and tube formation. Inhibition of PDPN expression by small interfering RNAs decreased cell adhesion in cultured human dermal lymphatic endothelial cells.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.











 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.