PARP Antibody (Clone 7A10)
Mouse Monoclonal Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, FC, ICC |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P09874 |
| Other Accession | NP_001609 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Clone Names | 7A10 |
| Calculated MW | 113084 Da |
| Gene ID | 142 |
|---|---|
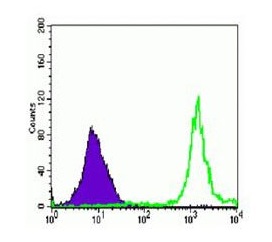
| Positive Control | Jurkat (1), K562 (2), HeLa (3), Raji (4), THP-1 (5) and SW620 (6) cell lysate. |
| Application & Usage | The antibody performs well on Western blot (1:500-1:2000) and Flow Cytometry studies (1:200-1:400). |
| Other Names | PARP, PPOL, ADPRT, ADPRT1, PARP-1, pADPRT-1, PARP1 |
| Target/Specificity | PARP |
| Antibody Form | Liquid |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Handling | The antibody solution should be gently mixed before use. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | -20 °C |
| Background Descriptions | |
| Precautions | PARP Antibody (Clone 7A10) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | PARP1 {ECO:0000303|PubMed:21680843, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:270} |
|---|---|
| Function | Poly-ADP-ribosyltransferase that mediates poly-ADP- ribosylation of proteins and plays a key role in DNA repair (PubMed:17177976, PubMed:18172500, PubMed:20388712, PubMed:19344625, PubMed:19661379, PubMed:21680843, PubMed:23230272, PubMed:25043379, PubMed:26344098, PubMed:32028527, PubMed:30104678, PubMed:33186521, PubMed:31796734, PubMed:32358582, PubMed:34737271, PubMed:34465625, PubMed:18055453, PubMed:22582261, PubMed:26626479, PubMed:26626480, PubMed:32241924). Mediates glutamate, aspartate, serine, histidine or tyrosine ADP-ribosylation of proteins: the ADP-D-ribosyl group of NAD(+) is transferred to the acceptor carboxyl group of target residues and further ADP-ribosyl groups are transferred to the 2'-position of the terminal adenosine moiety, building up a polymer with an average chain length of 20-30 units (PubMed:7852410, PubMed:9315851, PubMed:19764761, PubMed:25043379, PubMed:28190768, PubMed:29954836, PubMed:35393539). Serine ADP-ribosylation of proteins constitutes the primary form of ADP-ribosylation of proteins in response to DNA damage (PubMed:33186521, PubMed:34874266). Specificity for the different amino acids is conferred by interacting factors, such as HPF1 and NMNAT1 (PubMed:28190768, PubMed:29954836, PubMed:32028527, PubMed:33186521, PubMed:34874266, PubMed:34625544, PubMed:33589610). Following interaction with HPF1, catalyzes serine ADP-ribosylation of target proteins; HPF1 confers serine specificity by completing the PARP1 active site (PubMed:28190768, PubMed:29954836, PubMed:32028527, PubMed:33186521, PubMed:34874266, PubMed:34625544, PubMed:33589610). Also catalyzes tyrosine ADP-ribosylation of target proteins following interaction with HPF1 (PubMed:30257210, PubMed:29954836). Following interaction with NMNAT1, catalyzes glutamate and aspartate ADP- ribosylation of target proteins; NMNAT1 confers glutamate and aspartate specificity (By similarity). PARP1 initiates the repair of DNA breaks: recognizes and binds DNA breaks within chromatin and recruits HPF1, licensing serine ADP-ribosylation of target proteins, such as histones (H2BS6ADPr and H3S10ADPr), thereby promoting decompaction of chromatin and the recruitment of repair factors leading to the reparation of DNA strand breaks (PubMed:17177976, PubMed:18172500, PubMed:19344625, PubMed:19661379, PubMed:23230272, PubMed:27067600, PubMed:34874266, PubMed:34465625). HPF1 initiates serine ADP-ribosylation but restricts the polymerase activity of PARP1 in order to limit the length of poly- ADP-ribose chains (PubMed:34732825, PubMed:33683197, PubMed:34795260). In addition to base excision repair (BER) pathway, also involved in double-strand breaks (DSBs) repair: together with TIMELESS, accumulates at DNA damage sites and promotes homologous recombination repair by mediating poly-ADP-ribosylation (PubMed:26344098, PubMed:30356214). Mediates the poly-ADP-ribosylation of a number of proteins, including itself, APLF, CHFR, RPA1 and NFAT5 (PubMed:17396150, PubMed:19764761, PubMed:24906880, PubMed:34049076). In addition to proteins, also able to ADP-ribosylate DNA: catalyzes ADP-ribosylation of DNA strand break termini containing terminal phosphates and a 2'-OH group in single- and double-stranded DNA, respectively (PubMed:27471034). Required for PARP9 and DTX3L recruitment to DNA damage sites (PubMed:23230272). PARP1- dependent PARP9-DTX3L-mediated ubiquitination promotes the rapid and specific recruitment of 53BP1/TP53BP1, UIMC1/RAP80, and BRCA1 to DNA damage sites (PubMed:23230272). PARP1-mediated DNA repair in neurons plays a role in sleep: senses DNA damage in neurons and promotes sleep, facilitating efficient DNA repair (By similarity). In addition to DNA repair, also involved in other processes, such as transcription regulation, programmed cell death, membrane repair, adipogenesis and innate immunity (PubMed:17177976, PubMed:19344625, PubMed:15607977, PubMed:27256882, PubMed:32844745, PubMed:32315358, PubMed:35124853, PubMed:35460603, PubMed:35393539). Acts as a repressor of transcription: binds to nucleosomes and modulates chromatin structure in a manner similar to histone H1, thereby altering RNA polymerase II (PubMed:15607977, PubMed:22464733). Acts both as a positive and negative regulator of transcription elongation, depending on the context (PubMed:27256882, PubMed:35393539). Acts as a positive regulator of transcription elongation by mediating poly-ADP- ribosylation of NELFE, preventing RNA-binding activity of NELFE and relieving transcription pausing (PubMed:27256882). Acts as a negative regulator of transcription elongation in response to DNA damage by catalyzing poly-ADP-ribosylation of CCNT1, disrupting the phase separation activity of CCNT1 and subsequent activation of CDK9 (PubMed:35393539). Involved in replication fork progression following interaction with CARM1: mediates poly-ADP-ribosylation at replication forks, slowing fork progression (PubMed:33412112). Poly-ADP-ribose chains generated by PARP1 also play a role in poly-ADP-ribose-dependent cell death, a process named parthanatos (By similarity). Also acts as a negative regulator of the cGAS-STING pathway (PubMed:32844745, PubMed:32315358, PubMed:35460603). Acts by mediating poly-ADP- ribosylation of CGAS: PARP1 translocates into the cytosol following phosphorylation by PRKDC and catalyzes poly-ADP-ribosylation and inactivation of CGAS (PubMed:35460603). Acts as a negative regulator of adipogenesis: catalyzes poly-ADP-ribosylation of histone H2B on 'Glu- 35' (H2BE35ADPr) following interaction with NMNAT1, inhibiting phosphorylation of H2B at 'Ser-36' (H2BS36ph), thereby blocking expression of pro-adipogenetic genes (By similarity). Involved in the synthesis of ATP in the nucleus, together with NMNAT1, PARG and NUDT5 (PubMed:27257257). Nuclear ATP generation is required for extensive chromatin remodeling events that are energy-consuming (PubMed:27257257). |
| Cellular Location | Chromosome. Nucleus. Nucleus, nucleolus. Cytoplasm, cytosol. Note=Localizes to sites of DNA damage (PubMed:23230272, PubMed:26344098, PubMed:27568560, PubMed:30675909, PubMed:34625544, PubMed:34795260, PubMed:32358582, PubMed:22683995, PubMed:32241924). Recognizes (via PARP-type zinc-fingers) and binds DNA strand breaks (PubMed:22683995). Also binds normal/undamaged chromatin (PubMed:15607977). Auto poly-ADP-ribosylation promotes dissociation from chromatin (PubMed:15607977, PubMed:30675909, PubMed:32358582, PubMed:34625544). Extracted from chromatin by VCP/p97 following sumoylation and ubiquitination (PubMed:35013556). Translocates from the nucleus to the cytosol following phosphorylation by PRKDC (PubMed:35460603). Recruited to replication forks following interaction with CARM1 (PubMed:33412112). [Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 1, processed C- terminus]: Cytoplasm. Note=Following cleavage by caspase-3 (CASP3) and caspase-7 (CASP7) in response to apoptosis, translocates into the cytoplasm, where the auto-poly-ADP- ribosylated form serves as a poly-ADP-ribose carrier to induce AIFM1- mediated apoptosis. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
PARP, a 116 kDa nuclear poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase, appears to be involved in DNA repair in response to environmental stress. This protein can be cleaved by many ICE-like Caspases in vitro and is one of the main cleavage targets of caspase-3 in vivo. In human PARP, the cleavage occurs between Asp214 and Gly215, which separates the PARP amino-terminal DNA binding domain (24 kDa) from the carboxy-terminal catalytic domain (89 kDa). PARP helps cells to maintain their viability; cleavage of PARP facilitates cellular disassembly and serves as a marker of cells undergoing apoptosis.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.











 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.