Bok Antibody
Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q9UMX3 |
| Other Accession | EAW71269 |
| Reactivity | Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Calculated MW | 23280 Da |
| Gene ID | 666 |
|---|---|
| Application & Usage | Western blot analysis (0.5-4 µg/ml). |
| Other Names | Bcl-2-related ovarian killer |
| Target/Specificity | Bok |
| Antibody Form | Liquid |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Formulation | 100 µg (0.2 mg/ml) peptide affinity purified rabbit anti-Bok polyclonal antibody in phosphate buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.2, containing 50% glycerol, 1% BSA, 0.02% thimerosal. |
| Handling | The antibody solution should be gently mixed before use. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | -20 °C |
| Background Descriptions | |
| Precautions | Bok Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | BOK (HGNC:1087) |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | BCL2L9 |
| Function | [Isoform 1]: Apoptosis regulator that functions through different apoptotic signaling pathways (PubMed:27076518, PubMed:15102863, PubMed:20673843). Plays a roles as pro-apoptotic protein that positively regulates intrinsic apoptotic process in a BAX- and BAK1-dependent manner or in a BAX- and BAK1-independent manner (PubMed:27076518, PubMed:15102863). In response to endoplasmic reticulum stress promotes mitochondrial apoptosis through downstream BAX/BAK1 activation and positive regulation of PERK-mediated unfolded protein response (By similarity). Activates apoptosis independently of heterodimerization with survival-promoting BCL2 and BCL2L1 through induction of mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization, in a BAX- and BAK1-independent manner, in response to inhibition of ERAD- proteasome degradation system, resulting in cytochrome c release (PubMed:27076518). In response to DNA damage, mediates intrinsic apoptotic process in a TP53-dependent manner (PubMed:15102863). Plays a role in granulosa cell apoptosis by CASP3 activation (PubMed:20673843). Plays a roles as anti-apoptotic protein during neuronal apoptotic process, by negatively regulating poly ADP-ribose polymerase-dependent cell death through regulation of neuronal calcium homeostasis and mitochondrial bioenergetics in response to NMDA excitation (By similarity). In addition to its role in apoptosis, may regulate trophoblast cell proliferation during the early stages of placental development, by acting on G1/S transition through regulation of CCNE1 expression (PubMed:19942931). May also play a role as an inducer of autophagy by disrupting interaction between MCL1 and BECN1 (PubMed:24113155). |
| Cellular Location | [Isoform 1]: Mitochondrion membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O35425}; Single-pass membrane protein {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O35425}. Endoplasmic reticulum membrane; Single-pass membrane protein {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O35425}. Mitochondrion inner membrane. Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Mitochondrion. Endoplasmic reticulum. Mitochondrion outer membrane. Early endosome membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O35425}. Recycling endosome membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O35425}. Nucleus outer membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O35425}. Golgi apparatus, cis-Golgi network membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O35425}. Golgi apparatus, trans-Golgi network membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O35425}. Membrane. Note=Nuclear and cytoplasmic compartments in the early stages of apoptosis and during apoptosis it associates with mitochondria (PubMed:19942931). In healthy cells, associates loosely with the membrane in a hit-and-run mode. The insertion and accumulation on membranes is enhanced through the activity of death signals, resulting in the integration of the membrane-bound protein into the membrane (PubMed:15868100). The transmembrane domain controls subcellular localization; constitutes a tail-anchor. Localizes in early and late endosome upon blocking of apoptosis. Must localize to the mitochondria to induce mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization and apoptosis (By similarity) {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O35425, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15868100, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19942931} |
| Tissue Location | Expressed mainly in oocytes; weak expression in granulosa cells of the developing follicles. In adult human ovaries, expressed in granulosa cells at all follicular stages, but expression in primordial/primary follicles granulosa cell is stronger than in secondary and antral follicles. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Bok (Bcl-2-related ovarian killer) is a pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family protein identified in the ovary based on its dimerization with the anti-apoptotic protein Mcl-1. In addition to the Bcl-2 homology (BH) domains 1 and 2 and the transmembrane sequence, Bok also has a BH3 domain believed to be important for dimerization with selective anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins and cell killing. Bok interacts strongly with some (Mcl-1, BHRF1, and Bfl-1) but not other (Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, and Bcl-w) anti-apoptotic members. In addition, cell killing induced by Bok was suppressed following coexpression with Mcl-1 and BHRF1, but not with Bcl-2, further indicating that Bok heterodimerized only with selective anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins. Bok was highly expressed in the ovary, testis and uterus.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.




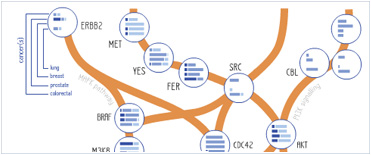







 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.

