JMJD6 Antibody
Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q6NYC1 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Opossum, Chimpanzee, Bovine |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Calculated MW | 46462 Da |
| Gene ID | 23210 |
|---|---|
| Positive Control | Western blot: Human brain lysate, mouse brain lysate |
| Application & Usage | Western blot: 0.25-1.0 µg/ml. However, the optimal conditions should be determined individually. |
| Other Names | Jumonji Domain Containing 6; PTDSR |
| Target/Specificity | JMJD6 |
| Antibody Form | Liquid |
| Appearance | Colorless liquid |
| Formulation | 50 µg of antibody in 100 µl PBS containing 0.05% BSA and 0.05% sodium salt. |
| Handling | The antibody solution should be gently mixed before use. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | -20 °C |
| Background Descriptions | |
| Precautions | JMJD6 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | JMJD6 (HGNC:19355) |
|---|---|
| Function | Dioxygenase that can both act as a arginine demethylase and a lysyl-hydroxylase (PubMed:24498420, PubMed:17947579, PubMed:20684070, PubMed:21060799, PubMed:22189873). Acts as a lysyl-hydroxylase that catalyzes 5-hydroxylation on specific lysine residues of target proteins such as U2AF2/U2AF65 and LUC7L2. Regulates RNA splicing by mediating 5-hydroxylation of U2AF2/U2AF65, affecting the pre-mRNA splicing activity of U2AF2/U2AF65 (PubMed:19574390). Hydroxylates its own N-terminus, which is required for homooligomerization (PubMed:22189873). Plays a role in the regulation of nucleolar liquid- liquid phase separation (LLPS) by post-translationally modifying LIAT1 at its lysine-rich domain which inhibits LIAT1 nucleolar targeting (By similarity). In addition to peptidyl-lysine 5-dioxygenase activity, may act as an RNA hydroxylase, as suggested by its ability to bind single strand RNA (PubMed:20679243, PubMed:29176719). Also acts as an arginine demethylase which preferentially demethylates asymmetric dimethylation (PubMed:17947579, PubMed:24498420, PubMed:24360279). Demethylates histone H3 at 'Arg-2' (H3R2me) and histone H4 at 'Arg-3' (H4R3me), including mono-, symmetric di- and asymmetric dimethylated forms, thereby playing a role in histone code (PubMed:17947579, PubMed:24360279). However, histone arginine demethylation may not constitute the primary activity in vivo (PubMed:17947579, PubMed:21060799, PubMed:22189873). In collaboration with BRD4, interacts with the positive transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFb) complex in its active form to regulate polymerase II promoter-proximal pause release for transcriptional activation of a large cohort of genes. On distal enhancers, so called anti-pause enhancers, demethylates both histone H4R3me2 and the methyl cap of 7SKsnRNA leading to the dismissal of the 7SKsnRNA:HEXIM1 inhibitor complex. After removal of repressive marks, the complex BRD4:JMJD6 attract and retain the P-TEFb complex on chromatin, leading to its activation, promoter-proximal polymerase II pause release, and transcriptional activation (PubMed:24360279). Demethylates other arginine methylated- proteins such as ESR1 (PubMed:24498420). Has no histone lysine demethylase activity (PubMed:21060799). Required for differentiation of multiple organs during embryogenesis. Acts as a key regulator of hematopoietic differentiation: required for angiogenic sprouting by regulating the pre-mRNA splicing activity of U2AF2/U2AF65 (By similarity). Seems to be necessary for the regulation of macrophage cytokine responses (PubMed:15622002). |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus, nucleoplasm. Nucleus, nucleolus. Cytoplasm. Note=Mainly found throughout the nucleoplasm outside of regions containing heterochromatic DNA, with some localization in nucleolus. During mitosis, excluded from the nucleus and reappears in the telophase of the cell cycle. |
| Tissue Location | Highly expressed in the heart, skeletal muscle and kidney. Expressed at moderate or low level in brain, placenta, lung, liver, pancreas, spleen, thymus, prostate, testis and ovary. Up- regulated in many patients with chronic pancreatitis. Expressed in nursing thymic epithelial cells. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Tudor domains are small protein structural motifs of about ~50 amino acids related to the “royal family” of methyl readers, which also includes chromo, MBT, PWWP, and Agenet-like domains. Tudor domains occur either alone, in tandem, or with other domains and are found in many proteins that are involved in RNA metabolism, germ cell development, transposon silencing, DNA damage response, histone modification, and chromatin remodeling. The tudor domains recognize symmetric methylated arginine or methylated lysine residues. JMJD6 is a 403 amino acid nuclear protein lysyl-hydroxylase that has been reported to have arginine demethylase activity for histone H3 at ‘Arg-2’ and histone H4 at ‘Arg-3’. JMJD6 has been s µggested to function in the differentiation of multiple organs during embryogenesis and regulate hematopoietic differentiation and macrophage cytokine responses. First identified as a putative phosphatidylserine receptor involved in phagocytosis of apoptotic cells, JMJD6 was later indicated not to directly function in the clearance of apoptotic cells. It is ubiquitously expressed in most tissues and is upregulated in patients with chronic pancreatitis and upon cytokine treatment, but not upon TNF-α treatment.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.




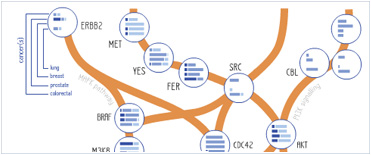







 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.

