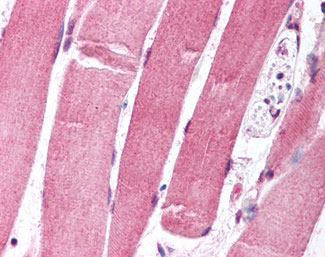
FOXO1 / FKHR Antibody (aa242-655, clone 7h3)
Mouse Monoclonal Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC-P |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q12778 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Clone Names | 7h3 |
| Calculated MW | 70kDa |
| Dilution | IHC-P (10 µg/ml), WB (0.1-2 µg/ml), |
| Gene ID | 2308 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Forkhead box protein O1, Forkhead box protein O1A, Forkhead in rhabdomyosarcoma, FOXO1, FKHR, FOXO1A |
| Target/Specificity | Fusion protein containing the region encoding aa 242-655 of human FKHR expressed in E. coli. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | Long term: -20°C; Short term: +4°C. Avoid repeat freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | FOXO1 / FKHR Antibody (aa242-655, clone 7h3) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | FOXO1 {ECO:0000303|PubMed:12228231, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:3819} |
|---|---|
| Function | Transcription factor that is the main target of insulin signaling and regulates metabolic homeostasis in response to oxidative stress (PubMed:10358076, PubMed:12228231, PubMed:15220471, PubMed:15890677, PubMed:18356527, PubMed:19221179, PubMed:20543840, PubMed:21245099). Binds to the insulin response element (IRE) with consensus sequence 5'-TT[G/A]TTTTG-3' and the related Daf-16 family binding element (DBE) with consensus sequence 5'-TT[G/A]TTTAC-3' (PubMed:10358076). Activity suppressed by insulin (PubMed:10358076). Main regulator of redox balance and osteoblast numbers and controls bone mass (By similarity). Orchestrates the endocrine function of the skeleton in regulating glucose metabolism (By similarity). Also acts as a key regulator of chondrogenic commitment of skeletal progenitor cells in response to lipid availability: when lipids levels are low, translocates to the nucleus and promotes expression of SOX9, which induces chondrogenic commitment and suppresses fatty acid oxidation (By similarity). Acts synergistically with ATF4 to suppress osteocalcin/BGLAP activity, increasing glucose levels and triggering glucose intolerance and insulin insensitivity (By similarity). Also suppresses the transcriptional activity of RUNX2, an upstream activator of osteocalcin/BGLAP (By similarity). Acts as an inhibitor of glucose sensing in pancreatic beta cells by acting as a transcription repressor and suppressing expression of PDX1 (By similarity). In hepatocytes, promotes gluconeogenesis by acting together with PPARGC1A and CEBPA to activate the expression of genes such as IGFBP1, G6PC1 and PCK1 (By similarity). Also promotes gluconeogenesis by directly promoting expression of PPARGC1A and G6PC1 (PubMed:17024043). Important regulator of cell death acting downstream of CDK1, PKB/AKT1 and STK4/MST1 (PubMed:18356527, PubMed:19221179). Promotes neural cell death (PubMed:18356527). Mediates insulin action on adipose tissue (By similarity). Regulates the expression of adipogenic genes such as PPARG during preadipocyte differentiation and, adipocyte size and adipose tissue-specific gene expression in response to excessive calorie intake (By similarity). Regulates the transcriptional activity of GADD45A and repair of nitric oxide-damaged DNA in beta-cells (By similarity). Required for the autophagic cell death induction in response to starvation or oxidative stress in a transcription-independent manner (PubMed:20543840). Mediates the function of MLIP in cardiomyocytes hypertrophy and cardiac remodeling (By similarity). Positive regulator of apoptosis in cardiac smooth muscle cells as a result of its transcriptional activation of pro-apoptotic genes (PubMed:19483080). Regulates endothelial cell (EC) viability and apoptosis in a PPIA/CYPA- dependent manner via transcription of CCL2 and BCL2L11 which are involved in EC chemotaxis and apoptosis (PubMed:31063815). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm. Nucleus Note=Shuttles between the cytoplasm and nucleus. Largely nuclear in unstimulated cells (PubMed:11311120, PubMed:12228231, PubMed:19221179, PubMed:21245099, PubMed:20543840, PubMed:25009184). In osteoblasts, colocalizes with ATF4 and RUNX2 in the nucleus (By similarity). Serum deprivation increases localization to the nucleus, leading to activate expression of SOX9 and subsequent chondrogenesis (By similarity) Insulin-induced phosphorylation at Ser-256 by PKB/AKT1 leads, via stimulation of Thr-24 phosphorylation, to binding of 14-3-3 proteins and nuclear export to the cytoplasm where it is degraded by the ubiquitin-proteasomal pathway (PubMed:11237865, PubMed:12228231) Phosphorylation at Ser-249 by CDK1 disrupts binding of 14-3-3 proteins and promotes nuclear accumulation (PubMed:18356527). Phosphorylation by NLK results in nuclear export (By similarity). Translocates to the nucleus upon oxidative stress-induced phosphorylation at Ser-212 by STK4/MST1 (PubMed:19221179, PubMed:21245099). SGK1-mediated phosphorylation also results in nuclear translocation (By similarity) Retained in the nucleus under stress stimuli including oxidative stress, nutrient deprivation or nitric oxide (By similarity). Retained in the nucleus on methylation (By similarity). PPIA/CYPA stimulates its nuclear accumulation (PubMed:31063815). Deacetylation by SIRT6, promotes its translocation into the cytoplasm (PubMed:25009184) {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9R1E0, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11237865, ECO:0000269|PubMed:11311120, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12228231, ECO:0000269|PubMed:18356527, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19221179, ECO:0000269|PubMed:20543840, ECO:0000269|PubMed:21245099, ECO:0000269|PubMed:25009184, ECO:0000269|PubMed:31063815} |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in umbilical endothelial cells (at protein level) (PubMed:19483080). Abundantly expressed in skeletal muscle and ovary, with lower expression in the heart, placenta, lung, liver, pancreas, spleen, testis and small intestine (PubMed:9479491) Weakly expressed in the brain, thymus, prostate and mucosal lining of the colon (PubMed:9479491). |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Transcription factor that is the main target of insulin signaling and regulates metabolic homeostasis in response to oxidative stress. Binds to the insulin response element (IRE) with consensus sequence 5'-TT[G/A]TTTTG-3' and the related Daf-16 family binding element (DBE) with consensus sequence 5'- TT[G/A]TTTAC-3'. Activity suppressed by insulin. Main regulator of redox balance and osteoblast numbers and controls bone mass. Orchestrates the endocrine function of the skeleton in regulating glucose metabolism. Acts synergistically with ATF4 to suppress osteocalcin/BGLAP activity, increasing glucose levels and triggering glucose intolerance and insulin insensitivity. Also suppresses the transcriptional activity of RUNX2, an upstream activator of osteocalcin/BGLAP. In hepatocytes, promotes gluconeogenesis by acting together with PPARGC1A to activate the expression of genes such as IGFBP1, G6PC and PPCK1. Important regulator of cell death acting downstream of CDK1, PKB/AKT1 and SKT4/MST1. Promotes neural cell death. Mediates insulin action on adipose. Regulates the expression of adipogenic genes such as PPARG during preadipocyte differentiation and, adipocyte size and adipose tissue-specific gene expression in response to excessive calorie intake. Regulates the transcriptional activity of GADD45A and repair of nitric oxide-damaged DNA in beta-cells. Required for the autophagic cell death induction in response to starvation or oxidative stress in a transcription-independent manner.
References
Galili N.,et al.Nat. Genet. 5:230-235(1993).
Anderson M.J.,et al.Genomics 47:187-199(1998).
Kalnine N.,et al.Submitted (MAY-2003) to the EMBL/GenBank/DDBJ databases.
Dunham A.,et al.Nature 428:522-528(2004).
Davis R.J.,et al.Cancer Res. 54:2869-2872(1994).
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.











 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.