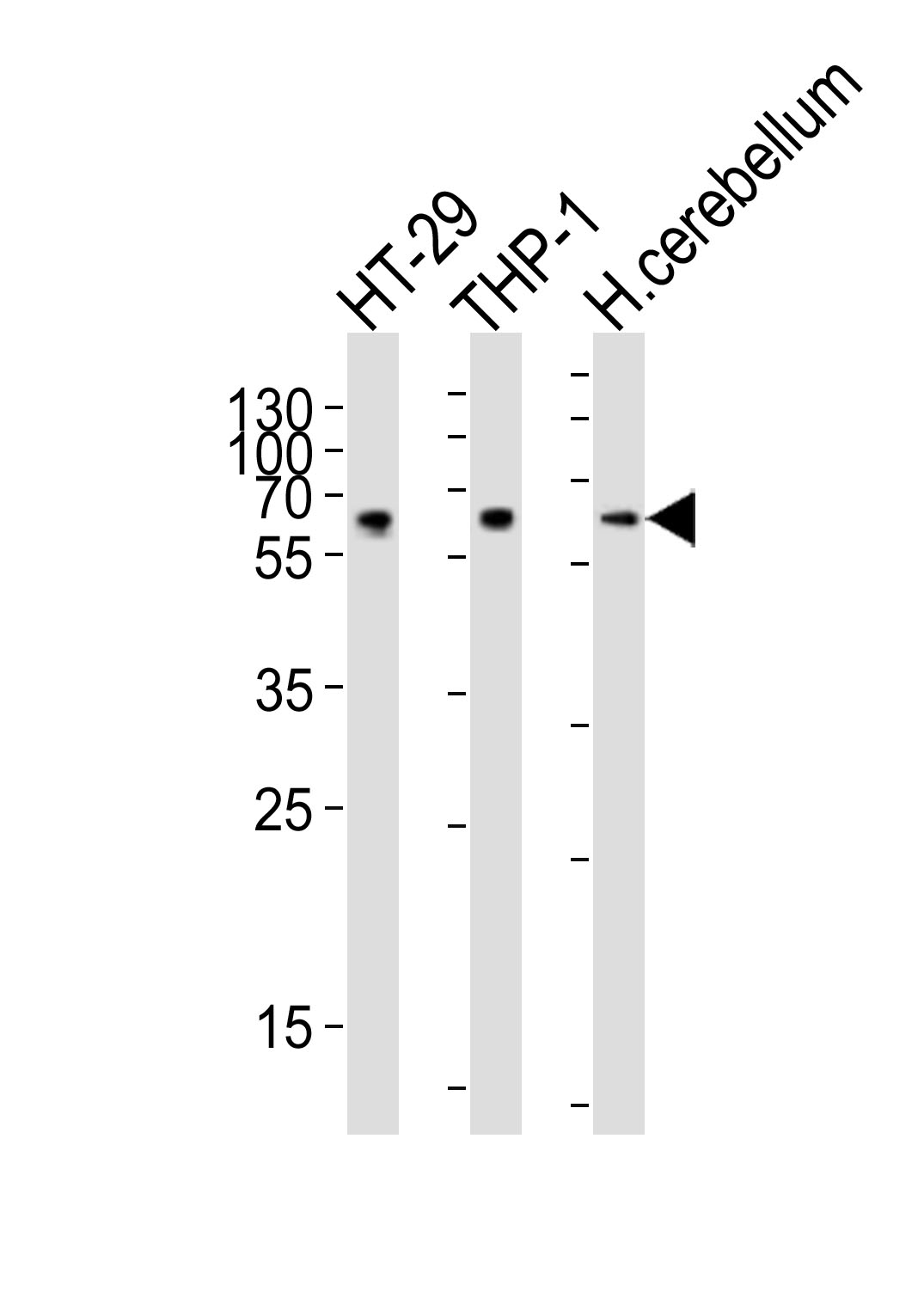
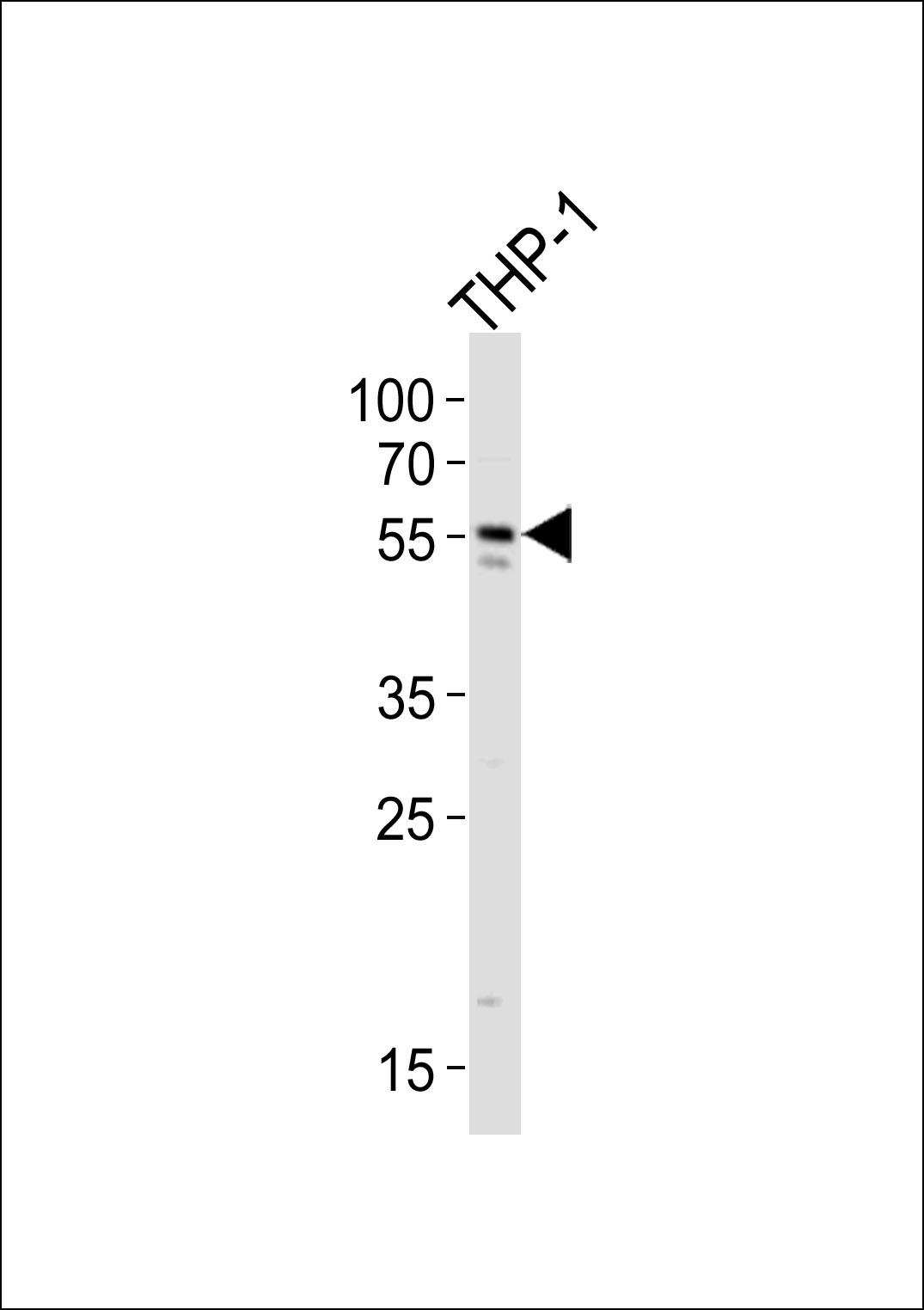
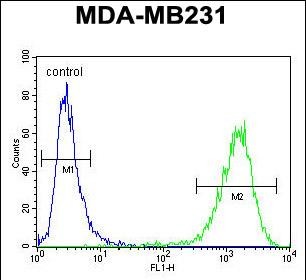
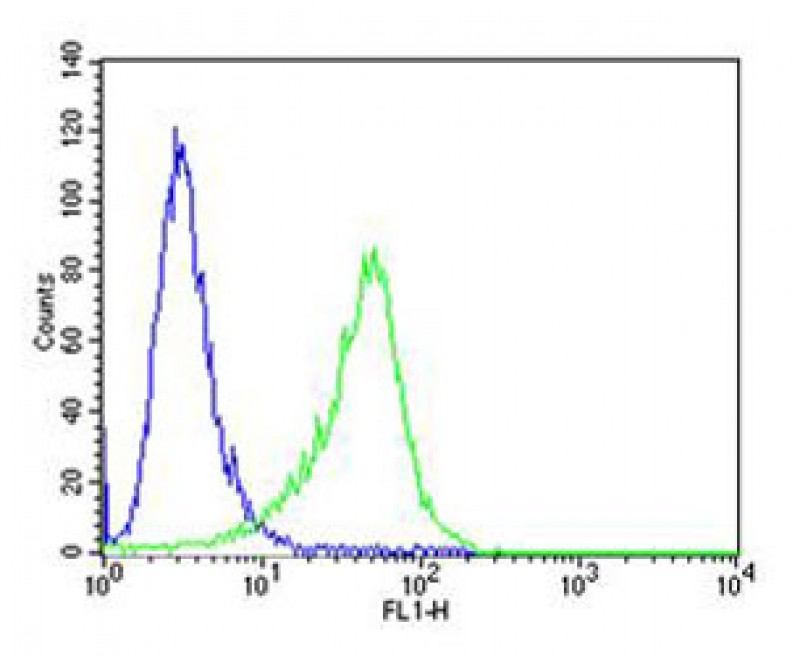
CF150 Antibody (Center)
Affinity Purified Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody (Pab)
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS: 3
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, FC, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q8N884 |
| Other Accession | NP_612450.2 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | Rabbit IgG |
| Calculated MW | 58814 Da |
| Antigen Region | 266-295 aa |
| Gene ID | 115004 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Cyclic GMP-AMP synthase, cGAMP synthase, cGAS, h-cGAS, Mab-21 domain-containing protein 1, MB21D1, C6orf150 |
| Target/Specificity | This CF150 antibody is generated from rabbits immunized with a KLH conjugated synthetic peptide between 266-295 amino acids from the Central region of human CF150. |
| Dilution | WB~~1:1000 FC~~1:25 |
| Format | Purified polyclonal antibody supplied in PBS with 0.09% (W/V) sodium azide. This antibody is purified through a protein A column, followed by peptide affinity purification. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 2 weeks. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | CF150 Antibody (Center) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | CGAS {ECO:0000303|PubMed:23258413, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:21367} |
|---|---|
| Function | Nucleotidyltransferase that catalyzes the formation of cyclic GMP-AMP (2',3'-cGAMP) from ATP and GTP and plays a key role in innate immunity (PubMed:23258413, PubMed:24077100, PubMed:25131990, PubMed:23707061, PubMed:23722159, PubMed:29976794, PubMed:30799039, PubMed:21478870, PubMed:23707065, PubMed:24116191, PubMed:24462292, PubMed:32814054, PubMed:33273464, PubMed:26300263, PubMed:33542149, PubMed:31142647, PubMed:37217469, PubMed:37802025). Catalysis involves both the formation of a 2',5' phosphodiester linkage at the GpA step and the formation of a 3',5' phosphodiester linkage at the ApG step, producing c[G(2',5')pA(3',5')p] (PubMed:28214358, PubMed:28363908). Acts as a key DNA sensor: directly binds double-stranded DNA (dsDNA), inducing the formation of liquid-like droplets in which CGAS is activated, leading to synthesis of 2',3'-cGAMP, a second messenger that binds to and activates STING1, thereby triggering type-I interferon production (PubMed:28314590, PubMed:28363908, PubMed:29976794, PubMed:33230297, PubMed:32817552, PubMed:33606975, PubMed:35438208, PubMed:35460603, PubMed:35322803, PubMed:35503863). Preferentially recognizes and binds curved long dsDNAs of a minimal length of 40 bp (PubMed:30007416). Acts as a key foreign DNA sensor, the presence of double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) in the cytoplasm being a danger signal that triggers the immune responses (PubMed:28363908). Has antiviral activity by sensing the presence of dsDNA from DNA viruses in the cytoplasm (PubMed:28363908). Also acts as an innate immune sensor of infection by retroviruses, such as HIV-2, by detecting the presence of reverse- transcribed DNA in the cytosol (PubMed:23929945, PubMed:24269171, PubMed:30270045, PubMed:32852081). In contrast, HIV-1 is poorly sensed by CGAS, due to its capsid that cloaks viral DNA from CGAS detection (PubMed:24269171, PubMed:30270045, PubMed:32852081). Detection of retroviral reverse-transcribed DNA in the cytosol may be indirect and be mediated via interaction with PQBP1, which directly binds reverse- transcribed retroviral DNA (PubMed:26046437). Also detects the presence of DNA from bacteria, such as M.tuberculosis (PubMed:26048138). 2',3'- cGAMP can be transferred from producing cells to neighboring cells through gap junctions, leading to promote STING1 activation and convey immune response to connecting cells (PubMed:24077100). 2',3'-cGAMP can also be transferred between cells by virtue of packaging within viral particles contributing to IFN-induction in newly infected cells in a cGAS-independent but STING1-dependent manner (PubMed:26229115). Also senses the presence of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) that are translocated to the cytosol following phagocytosis, leading to synthesis of 2',3'-cGAMP (PubMed:33688080). In addition to foreign DNA, can also be activated by endogenous nuclear or mitochondrial DNA (PubMed:31299200, PubMed:28738408, PubMed:28759889, PubMed:33230297, PubMed:33031745). When self-DNA leaks into the cytosol during cellular stress (such as mitochondrial stress, SARS-CoV-2 infection causing severe COVID-19 disease, DNA damage, mitotic arrest or senescence), or is present in form of cytosolic micronuclei, CGAS is activated leading to a state of sterile inflammation (PubMed:31299200, PubMed:28738408, PubMed:28759889, PubMed:33230297, PubMed:33031745, PubMed:35045565). Acts as a regulator of cellular senescence by binding to cytosolic chromatin fragments that are present in senescent cells, leading to trigger type-I interferon production via STING1 and promote cellular senescence (By similarity). Also involved in the inflammatory response to genome instability and double-stranded DNA breaks: acts by localizing to micronuclei arising from genome instability (PubMed:28738408, PubMed:28759889). Micronuclei, which are frequently found in cancer cells, consist of chromatin surrounded by their own nuclear membrane: following breakdown of the micronuclear envelope, a process associated with chromothripsis, CGAS binds self-DNA exposed to the cytosol, leading to 2',3'-cGAMP synthesis and subsequent activation of STING1 and type-I interferon production (PubMed:28738408, PubMed:28759889). Activated in response to prolonged mitotic arrest, promoting mitotic cell death (PubMed:31299200). In a healthy cell, CGAS is however kept inactive even in cellular events that directly expose it to self-DNA, such as mitosis, when cGAS associates with chromatin directly after nuclear envelope breakdown or remains in the form of postmitotic persistent nuclear cGAS pools bound to chromatin (PubMed:31299200, PubMed:33542149). Nuclear CGAS is inactivated by chromatin via direct interaction with nucleosomes, which block CGAS from DNA binding and thus prevent CGAS-induced autoimmunity (PubMed:31299200, PubMed:33542149, PubMed:33051594, PubMed:32911482, PubMed:32912999). Also acts as a suppressor of DNA repair in response to DNA damage: inhibits homologous recombination repair by interacting with PARP1, the CGAS-PARP1 interaction leading to impede the formation of the PARP1-TIMELESS complex (PubMed:30356214, PubMed:31544964). In addition to DNA, also sense translation stress: in response to translation stress, translocates to the cytosol and associates with collided ribosomes, promoting its activation and triggering type-I interferon production (PubMed:34111399). In contrast to other mammals, human CGAS displays species-specific mechanisms of DNA recognition and produces less 2',3'-cGAMP, allowing a more fine-tuned response to pathogens (PubMed:30007416). |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus. Chromosome. Cell membrane; Peripheral membrane protein. Cytoplasm, cytosol. Note=Mainly localizes in the nucleus, and at low level in the cytosol (PubMed:31808743, PubMed:31544964). On chromosomes, enriched on centromeric satellite and LINE DNA repeat elements (PubMed:30811988) Exported from the nucleus to the cytosol in a XPO1/CRM1 via the nuclear export signal in response to DNA stimulation (PubMed:33406424). Outside the nucleus, localizes at the cell membrane as a peripheral membrane protein in resting conditions: association to the cell membrane is mediated via binding to phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PtdIns(4,5)P2) (PubMed:30827685). Localization at the cell membrane is required to limit the recognition of self-DNA (PubMed:30827685) Following detection of double-stranded DNA (dsDNA), released from the cell membrane into the cytosol in order to signal (PubMed:30827685) Upon transfection with dsDNA forms punctate structures that co-localize with DNA and Beclin-1 (BECN1) (PubMed:26048138). Phosphorylation at Tyr-215 promotes cytosolic retention (PubMed:30356214). In response to translation stress, translocates to the cytosol and associates with collided ribosomes (PubMed:34111399). |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in the monocytic cell line THP1. |

Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
The exact function of C6orf150 remains unknown.
References
Rush, J., et al. Nat. Biotechnol. 23(1):94-101(2005)
Rush, J., et al. Nat. Biotechnol. 23(1):94-101(2005)
Mungall, A.J., et al. Nature 425(6960):805-811(2003)
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.





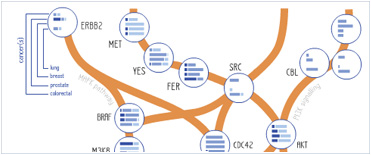







 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.