SIRT2 Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC-P, IF, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q8IXJ6 |
| Other Accession | NP_036369, 13775600 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 43182 Da |
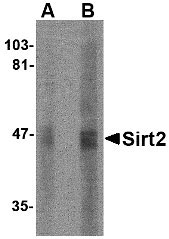
| Application Notes | SIRT2 antibody can be used for detection of SIRT2 by Western blot at 2.5 - 5 µg/mL. Antibody can also be used for immunohistochemistry starting at 2.5 µg/mL. For immunofluorescence start at 20 µg/mL. |
| Gene ID | 22933 |
|---|---|
| Target/Specificity | SIRT2; |
| Reconstitution & Storage | SIRT2 antibody can be stored at 4℃ for three months and -20℃, stable for up to one year. As with all antibodies care should be taken to avoid repeated freeze thaw cycles. Antibodies should not be exposed to prolonged high temperatures. |
| Precautions | SIRT2 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | SIRT2 |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | SIR2L, SIR2L2 |
| Function | NAD-dependent protein deacetylase, which deacetylates internal lysines on histone and alpha-tubulin as well as many other proteins such as key transcription factors (PubMed:24177535, PubMed:12620231, PubMed:16648462, PubMed:18249187, PubMed:18332217, PubMed:18995842, PubMed:20587414, PubMed:21081649, PubMed:20543840, PubMed:22014574, PubMed:21726808, PubMed:21949390, PubMed:22771473, PubMed:23468428, PubMed:23908241, PubMed:24940000, PubMed:24769394, PubMed:24681946). Participates in the modulation of multiple and diverse biological processes such as cell cycle control, genomic integrity, microtubule dynamics, cell differentiation, metabolic networks, and autophagy (PubMed:24177535, PubMed:12620231, PubMed:16648462, PubMed:18249187, PubMed:18332217, PubMed:18995842, PubMed:20587414, PubMed:21081649, PubMed:20543840, PubMed:22014574, PubMed:21726808, PubMed:21949390, PubMed:22771473, PubMed:23468428, PubMed:23908241, PubMed:24940000, PubMed:24769394, PubMed:24681946). Plays a major role in the control of cell cycle progression and genomic stability (PubMed:12697818, PubMed:17488717, PubMed:16909107, PubMed:17726514, PubMed:19282667, PubMed:23468428). Functions in the antephase checkpoint preventing precocious mitotic entry in response to microtubule stress agents, and hence allowing proper inheritance of chromosomes (PubMed:12697818, PubMed:17488717, PubMed:16909107, PubMed:17726514, PubMed:19282667, PubMed:23468428). Positively regulates the anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) ubiquitin ligase complex activity by deacetylating CDC20 and FZR1, then allowing progression through mitosis (PubMed:22014574). Associates both with chromatin at transcriptional start sites (TSSs) and enhancers of active genes (PubMed:23468428). Plays a role in cell cycle and chromatin compaction through epigenetic modulation of the regulation of histone H4 'Lys-20' methylation (H4K20me1) during early mitosis (PubMed:23468428). Specifically deacetylates histone H4 at 'Lys-16' (H4K16ac) between the G2/M transition and metaphase enabling H4K20me1 deposition by KMT5A leading to ulterior levels of H4K20me2 and H4K20me3 deposition throughout cell cycle, and mitotic S-phase progression (PubMed:23468428). Deacetylates KMT5A modulating KMT5A chromatin localization during the mitotic stress response (PubMed:23468428). Deacetylates also histone H3 at 'Lys-57' (H3K56ac) during the mitotic G2/M transition (PubMed:20587414). Upon bacterium Listeria monocytogenes infection, deacetylates 'Lys-18' of histone H3 in a receptor tyrosine kinase MET- and PI3K/Akt-dependent manner, thereby inhibiting transcriptional activity and promoting late stages of listeria infection (PubMed:23908241). During oocyte meiosis progression, may deacetylate histone H4 at 'Lys-16' (H4K16ac) and alpha-tubulin, regulating spindle assembly and chromosome alignment by influencing microtubule dynamics and kinetochore function (PubMed:24940000). Deacetylates histone H4 at 'Lys-16' (H4K16ac) at the VEGFA promoter and thereby contributes to regulate expression of VEGFA, a key regulator of angiogenesis (PubMed:24940000). Deacetylates alpha- tubulin at 'Lys-40' and hence controls neuronal motility, oligodendroglial cell arbor projection processes and proliferation of non-neuronal cells (PubMed:18332217, PubMed:18995842). Phosphorylation at Ser-368 by a G1/S-specific cyclin E-CDK2 complex inactivates SIRT2- mediated alpha-tubulin deacetylation, negatively regulating cell adhesion, cell migration and neurite outgrowth during neuronal differentiation (PubMed:17488717). Deacetylates PARD3 and participates in the regulation of Schwann cell peripheral myelination formation during early postnatal development and during postinjury remyelination (PubMed:21949390). Involved in several cellular metabolic pathways (PubMed:20543840, PubMed:21726808, PubMed:24769394). Plays a role in the regulation of blood glucose homeostasis by deacetylating and stabilizing phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase PCK1 activity in response to low nutrient availability (PubMed:21726808). Acts as a key regulator in the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) by deacetylating and activating the glucose-6-phosphate G6PD enzyme, and therefore, stimulates the production of cytosolic NADPH to counteract oxidative damage (PubMed:24769394). Maintains energy homeostasis in response to nutrient deprivation as well as energy expenditure by inhibiting adipogenesis and promoting lipolysis (PubMed:20543840). Attenuates adipocyte differentiation by deacetylating and promoting FOXO1 interaction to PPARG and subsequent repression of PPARG-dependent transcriptional activity (PubMed:20543840). Plays a role in the regulation of lysosome- mediated degradation of protein aggregates by autophagy in neuronal cells (PubMed:20543840). Deacetylates FOXO1 in response to oxidative stress or serum deprivation, thereby negatively regulating FOXO1- mediated autophagy (PubMed:20543840). Deacetylates a broad range of transcription factors and co-regulators regulating target gene expression. Deacetylates transcriptional factor FOXO3 stimulating the ubiquitin ligase SCF(SKP2)-mediated FOXO3 ubiquitination and degradation (By similarity). Deacetylates HIF1A and therefore promotes HIF1A degradation and inhibition of HIF1A transcriptional activity in tumor cells in response to hypoxia (PubMed:24681946). Deacetylates RELA in the cytoplasm inhibiting NF-kappaB-dependent transcription activation upon TNF-alpha stimulation (PubMed:21081649). Inhibits transcriptional activation by deacetylating p53/TP53 and EP300 (PubMed:18249187, PubMed:18995842). Deacetylates also EIF5A (PubMed:22771473). Functions as a negative regulator on oxidative stress-tolerance in response to anoxia-reoxygenation conditions (PubMed:24769394). Plays a role as tumor suppressor (PubMed:22014574). In addition to protein deacetylase activity, also has activity toward long-chain fatty acyl groups and mediates protein-lysine demyristoylation and depalmitoylation of target proteins, such as ARF6 and KRAS, thereby regulating their association with membranes (PubMed:25704306, PubMed:29239724, PubMed:32103017). |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus. Cytoplasm, perinuclear region {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8VDQ8}. Cytoplasm. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome, centriole Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, spindle. Midbody. Chromosome. Perikaryon {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8VDQ8}. Cell projection {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8VDQ8}. Cell projection, growth cone {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8VDQ8}. Myelin membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8VDQ8}. Note=Localizes in the cytoplasm during most of the cell cycle except in the G2/M transition and during mitosis, where it is localized in association with chromatin and induces deacetylation of histone at 'Lys-16' (H4K16ac) (PubMed:17726514, PubMed:23468428). Colocalizes with KMT5A at mitotic foci (PubMed:23468428). Colocalizes with CDK1 at centrosome during prophase and splindle fibers during metaphase (PubMed:17488717) Colocalizes with Aurora kinase AURKA at centrosome during early prophase and in the centrioles and growing mitotic spindle throughout metaphase (PubMed:17488717). Colocalizes with Aurora kinase AURKB during cytokinesis with the midbody (PubMed:17488717). Colocalizes with microtubules (PubMed:12620231). Detected in perinuclear foci that may be aggresomes containing misfolded, ubiquitinated proteins (By similarity). Shuttles between the cytoplasm and the nucleus through the CRM1 export pathway (PubMed:17726514). Colocalizes with EP300 in the nucleus (PubMed:24177535). Translocates to the nucleus and chromatin upon bacterium Listeria monocytogenes infection in interphase cells (PubMed:23908241). Deacetylates FOXO3 in the cytoplasm (By similarity) Colocalizes with PLP1 in internodal regions, at paranodal axoglial junction and Schmidt-Lanterman incisures of myelin sheath (By similarity). Colocalizes with CDK5R1 in the perikaryon, neurites and growth cone of hippocampal neurons (By similarity). Colocalizes with alpha-tubulin in neuronal growth cone (By similarity). Localizes in the cytoplasm and nucleus of germinal vesicle (GV) stage oocytes (By similarity). Colocalizes with alpha-tubulin on the meiotic spindle as the oocytes enter into metaphase, and also during meiotic anaphase and telophase, especially with the midbody (By similarity). Colocalizes with PARD3 in internodal region of axons (By similarity). Colocalizes with acetylated alpha-tubulin in cell projection processes during primary oligodendrocyte precursor (OLP) differentiation (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q8VDQ8, ECO:0000269|PubMed:12620231, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17488717, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17726514, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23468428, ECO:0000269|PubMed:23908241, ECO:0000269|PubMed:24177535} [Isoform 2]: Cytoplasm. Nucleus Note=Predominantly localized in the cytoplasmic |
| Tissue Location | Isoform 1 is expressed in heart, liver and skeletal muscle, weakly expressed in the cortex. Isoform 2 is strongly expressed in the cortex, weakly expressed in heart and liver. Weakly expressed in several malignancies including breast, liver, brain, kidney and prostate cancers compared to normal tissues. Weakly expressed in glioma cell lines compared to normal brain tissues (at protein level). Widely expressed. Highly expressed in heart, brain and skeletal muscle, while it is weakly expressed in placenta and lung. Down-regulated in many gliomas suggesting that it may act as a tumor suppressor gene in human gliomas possibly through the regulation of microtubule network |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
SIRT2 Antibody: Autophagy, the process of bulk degradation of cellular proteins through an autophagosomic-lysosomal pathway is important for normal growth control and may be defective in tumor cells. It is involved in the preservation of cellular nutrients under starvation conditions as well as the normal turnover of cytosolic components. This process is negatively regulated by TOR (Target of rapamycin) through phosphorylation of autophagy protein APG1. ATG16, another member of the autophagy protein family, forms a complex with the ATG5-ATG12 conjugate. This multimeric protein has been shown to be essential for autophagosome formation in both yeast and mammals and targets the ATG5-ATG12 complex to the autophagic isolation membrane during the formation of the autophagosome. Because mammalian ATG16 has seven WD-repeats in its C-terminal domain, it has been suggested that these may form a platform for further protein-protein interactions. Multiple isoforms of ATG16 are known to exist.
References
Yamamoto H, Schoonjans K, and Auwerx J. Sirtuin functions in health and disease. Mol. Endocrinol.2007; 21:1745-55.
Frye RA. Characterization of five human cDNAs with homology to the yeast SIR2 gene: SIR2-like proteins (sirtuins) metabolize NAD and may have protein ADP-ribosyltransferase activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.1999; 260:273-279.
North BJ, Marshall BL, Borra MT, et. al. The human Sir2 ortholog, SIRT2, is an NAD+-dependent tubulin deacetylase. Mol. Cell.2003; 11:437-44.
Inoue T, Hiratsuka M, Osaki M, et al. The molecular biology of mammalian SIRT proteins: SIRT2 in cell cycle regulation. Cell Cycle2007; 6:1011-8.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.











 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.