PARK2 Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC-P, IF, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | O60260 |
| Other Accession | NP_004553, 169790969 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Isotype | IgG |
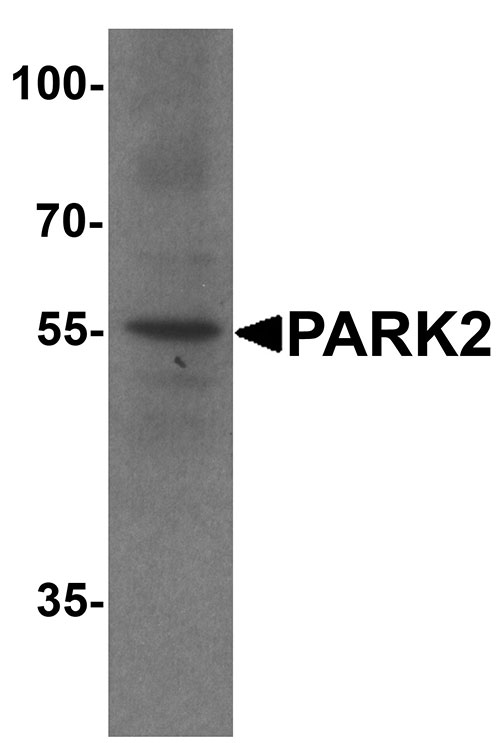
| Calculated MW | Predicted: 51 kDa Observed: 55 kDa |
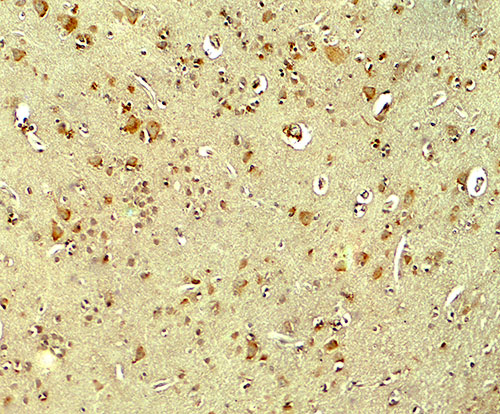
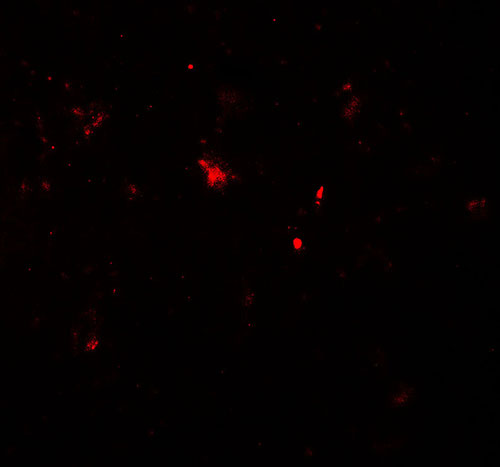
| Application Notes | PARK2 antibody can be used for detection of PARK2 by Western blot at 1 - 2 µg/ml. Antibody can also be used for Immunohistochemistry starting at 5 µg/mL. For immunofluorescence start at 20 µg/mL. |
| Gene ID | 5071 |
|---|---|
| Target/Specificity | PARK2; PARK2 antibody is human specific. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | PARK2 antibody can be stored at 4℃ for three months and -20℃, stable for up to one year. |
| Precautions | PARK2 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | PRKN (HGNC:8607) |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | PARK2 |
| Function | Functions within a multiprotein E3 ubiquitin ligase complex, catalyzing the covalent attachment of ubiquitin moieties onto substrate proteins (PubMed:10888878, PubMed:10973942, PubMed:11431533, PubMed:12150907, PubMed:12628165, PubMed:15105460, PubMed:16135753, PubMed:21376232, PubMed:21532592, PubMed:23754282, PubMed:23620051, PubMed:24660806, PubMed:24751536, PubMed:32047033, PubMed:29311685, PubMed:22396657). Substrates include SYT11 and VDAC1 (PubMed:32047033, PubMed:29311685). Other substrates are BCL2, CCNE1, GPR37, RHOT1/MIRO1, MFN1, MFN2, STUB1, SNCAIP, SEPTIN5, TOMM20, USP30, ZNF746, MIRO1 and AIMP2 (PubMed:10888878, PubMed:10973942, PubMed:11431533, PubMed:12150907, PubMed:12628165, PubMed:15105460, PubMed:16135753, PubMed:21376232, PubMed:21532592, PubMed:23754282, PubMed:23620051, PubMed:24660806, PubMed:24751536, PubMed:22396657). Mediates monoubiquitination as well as 'Lys-6', 'Lys-11', 'Lys-48'-linked and 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitination of substrates depending on the context (PubMed:19229105, PubMed:20889974, PubMed:25621951, PubMed:32047033, PubMed:25474007). Participates in the removal and/or detoxification of abnormally folded or damaged protein by mediating 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitination of misfolded proteins such as PARK7: 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitinated misfolded proteins are then recognized by HDAC6, leading to their recruitment to aggresomes, followed by degradation (PubMed:17846173, PubMed:19229105). Mediates 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitination of a 22 kDa O-linked glycosylated isoform of SNCAIP, possibly playing a role in Lewy-body formation (PubMed:11431533, PubMed:11590439, PubMed:15105460, PubMed:19229105, PubMed:15728840). Mediates monoubiquitination of BCL2, thereby acting as a positive regulator of autophagy (PubMed:20889974). Protects against mitochondrial dysfunction during cellular stress, by acting downstream of PINK1 to coordinate mitochondrial quality control mechanisms that remove and replace dysfunctional mitochondrial components (PubMed:32047033, PubMed:19029340, PubMed:19966284, PubMed:23620051, PubMed:24896179, PubMed:25527291, PubMed:18957282, PubMed:21376232, PubMed:22396657, PubMed:24660806, PubMed:25474007, PubMed:24784582, PubMed:11439185, PubMed:22082830, PubMed:23933751). Depending on the severity of mitochondrial damage and/or dysfunction, activity ranges from preventing apoptosis and stimulating mitochondrial biogenesis to regulating mitochondrial dynamics and eliminating severely damaged mitochondria via mitophagy (PubMed:32047033, PubMed:19029340, PubMed:19801972, PubMed:19966284, PubMed:23620051, PubMed:24896179, PubMed:25527291, PubMed:21376232, PubMed:22396657, PubMed:11439185, PubMed:22082830, PubMed:23933751, PubMed:33499712). Activation and recruitment onto the outer membrane of damaged/dysfunctional mitochondria (OMM) requires PINK1-mediated phosphorylation of both PRKN and ubiquitin (PubMed:24660806, PubMed:25474007, PubMed:24784582, PubMed:25527291). After mitochondrial damage, functions with PINK1 to mediate the decision between mitophagy or preventing apoptosis by inducing either the poly- or monoubiquitination of VDAC1, respectively; polyubiquitination of VDAC1 promotes mitophagy, while monoubiquitination of VDAC1 decreases mitochondrial calcium influx which ultimately inhibits apoptosis (PubMed:27534820, PubMed:32047033). When cellular stress results in irreversible mitochondrial damage, promotes the autophagic degradation of dysfunctional depolarized mitochondria (mitophagy) by promoting the ubiquitination of mitochondrial proteins such as TOMM20, RHOT1/MIRO1, MFN1 and USP30 (PubMed:19029340, PubMed:19966284, PubMed:21753002, PubMed:23620051, PubMed:24896179, PubMed:25527291, PubMed:22396657, PubMed:23933751). Preferentially assembles 'Lys-6'-, 'Lys-11'- and 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitin chains, leading to mitophagy (PubMed:25621951, PubMed:32047033). The PINK1-PRKN pathway also promotes fission of damaged mitochondria by PINK1-mediated phosphorylation which promotes the PRKN-dependent degradation of mitochondrial proteins involved in fission such as MFN2 (PubMed:23620051). This prevents the refusion of unhealthy mitochondria with the mitochondrial network or initiates mitochondrial fragmentation facilitating their later engulfment by autophagosomes (PubMed:23620051). Regulates motility of damaged mitochondria via the ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of MIRO1 and MIRO2; in motor neurons, this likely inhibits mitochondrial intracellular anterograde transport along the axons which probably increases the chance of the mitochondria undergoing mitophagy in the soma (PubMed:22396657). Involved in mitochondrial biogenesis via the 'Lys-48'-linked polyubiquitination of transcriptional repressor ZNF746/PARIS which leads to its subsequent proteasomal degradation and allows activation of the transcription factor PPARGC1A (PubMed:21376232). Limits the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) (PubMed:18541373). Regulates cyclin-E during neuronal apoptosis (PubMed:12628165). In collaboration with CHPF isoform 2, may enhance cell viability and protect cells from oxidative stress (PubMed:22082830). Independently of its ubiquitin ligase activity, protects from apoptosis by the transcriptional repression of p53/TP53 (PubMed:19801972). May protect neurons against alpha synuclein toxicity, proteasomal dysfunction, GPR37 accumulation, and kainate-induced excitotoxicity (PubMed:11439185). May play a role in controlling neurotransmitter trafficking at the presynaptic terminal and in calcium-dependent exocytosis. May represent a tumor suppressor gene (PubMed:12719539). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm, cytosol. Nucleus. Endoplasmic reticulum. Mitochondrion. Mitochondrion outer membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9WVS6}. Cell projection, neuron projection. Postsynaptic density {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9WVS6}. Presynapse {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q9WVS6}. Note=Mainly localizes in the cytosol (PubMed:19029340, PubMed:19229105). Co-localizes with SYT11 in neutrites (PubMed:12925569). Co-localizes with SNCAIP in brainstem Lewy bodies (PubMed:10319893, PubMed:11431533). Translocates to dysfunctional mitochondria that have lost the mitochondrial membrane potential; recruitment to mitochondria is PINK1-dependent (PubMed:24898855, PubMed:18957282, PubMed:19966284, PubMed:23620051) Mitochondrial localization also gradually increases with cellular growth (PubMed:22082830). |
| Tissue Location | Highly expressed in the brain including the substantia nigra (PubMed:9560156, PubMed:19501131). Expressed in heart, testis and skeletal muscle (PubMed:9560156). Expression is down- regulated or absent in tumor biopsies, and absent in the brain of PARK2 patients (PubMed:14614460, PubMed:12719539). Overexpression protects dopamine neurons from kainate-mediated apoptosis (PubMed:12628165) Found in serum (at protein level) (PubMed:19501131) |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disease whose symptoms include tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia, and postural instability (1). Mutations in the PARK2 gene are known to cause Parkinson disease and autosomal recessive juvenile Parkinson disease (2). The PARK2 protein is a component of a multiprotein E3 ubiquitin ligase complex that mediates the targeting of substrate proteins for proteasomal degradation (3). Recent studies have suggested that PARK2 expression reduces the mitochondrial accumulation of the apoptosis protein Bax under basal conditions and directly ubiquitinates Bax, thereby promoting cell survival (4).
References
Dauer W and Przedborski S. Parkinson’s disease: Mechanisms and models. Neuron 2003; 39:889-909.
Kitada T, Asakawa S, Hattori N, et al. Mutations in the parkin gene cause autosomal recessive juvenile parkinsonism. Nature 1998; 392:605-8.
Shimura H, Hattori N, Kubo Si, et al. Familial Parkinson disease gene product, parkin, is a ubiquitin-protein ligase. Nat. Genet. 2000; 25:302-5.
Johnson BN, Berger AK, Cortese GP, et al. The ubiquitin E3 ligase parkin regulates the proapoptotic function of Bax. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012; 109:6283-88.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.











 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.