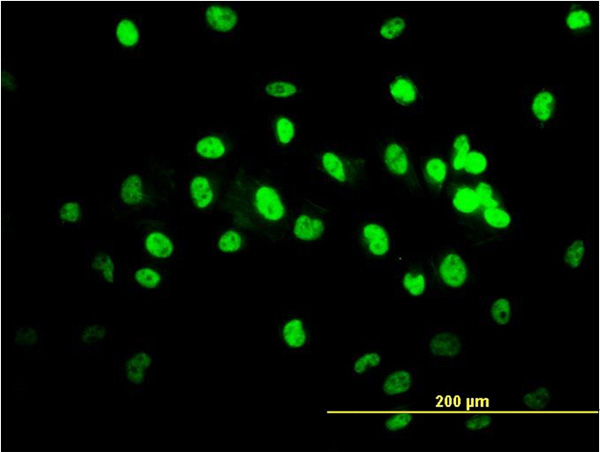
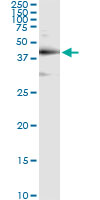
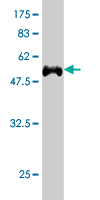
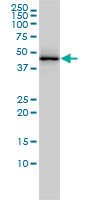
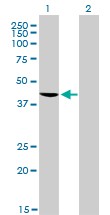
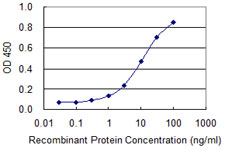
TARDBP Antibody (monoclonal) (M01)
Mouse monoclonal antibody raised against a full length recombinant TARDBP.
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, IHC, IF, IP |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q13148 |
| Other Accession | BC001487 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | mouse |
| Clonality | Monoclonal |
| Isotype | IgG1 Kappa |
| Clone Names | 2E2-D3 |
| Calculated MW | 44740 Da |
| Gene ID | 23435 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | TAR DNA-binding protein 43, TDP-43, TARDBP, TDP43 |
| Target/Specificity | TARDBP (AAH01487.1, 1 a.a. ~ 260 a.a) full-length recombinant protein with GST tag. MW of the GST tag alone is 26 KDa. |
| Dilution | WB~~1:500~1000 |
| Format | Clear, colorless solution in phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.2 . |
| Storage | Store at -20°C or lower. Aliquot to avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Precautions | TARDBP Antibody (monoclonal) (M01) is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
HIV-1, the causative agent of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS), contains an RNA genome that produces a chromosomally integrated DNA during the replicative cycle. Activation of HIV-1 gene expression by the transactivator Tat is dependent on an RNA regulatory element (TAR) located downstream of the transcription initiation site. The protein encoded by this gene is a transcriptional repressor that binds to chromosomally integrated TAR DNA and represses HIV-1 transcription. In addition, this protein regulates alternate splicing of the CFTR gene. A similar pseudogene is present on chromosome 20. [provided by RefSeq]
References
1.A 6.4 Mb Duplication of the α-Synuclein Locus Causing Frontotemporal Dementia and Parkinsonism: Phenotype-Genotype Correlations.Kara E, Kiely AP, Proukakis C, Giffin N, Love S, Hehir J, Rantell K, Pandraud A, Hernandez DG, Nacheva E, Pittman AM, Nalls MA, Singleton AB, Revesz T, Bhatia KP, Quinn N, Hardy J, Holton JL, Houlden HJAMA Neurol. 2014 Jul 7. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2014.994.2.UBE2E Ubiquitin-conjugating Enzymes and Ubiquitin Isopeptidase Y Regulate TDP-43 Protein Ubiquitination.Hans F, Fiesel FC, Strong JC, J?ckel S, Rasse TM, Geisler S, Springer W, Schulz JB, Voigt A, Kahle PJ.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jul 4;289(27):19164-79.3.Parkin-mediated reduction of nuclear and soluble TDP-43 reverses behavioral decline in symptomatic mice.Chen W, Lonskaya I, Hebron ML, Ibrahim Z, Olszewski RT, Neale JH, Moussa CE.Hum. Mol. Genet. (2014) doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddu2114.Interaction of transactive response DNA binding protein 43 with nuclear factor kappaB in mild cognitive impairment with episodic memory deficits.Ohta Y, Tremblay C, Schneider JA, Bennett DA, Calon F, Julien JPActa Neuropathol Commun. 2014 Apr 1;2(1):37.5.Casein Kinase II Induced Polymerization of Soluble TDP-43 into Filaments Is Inhibited by Heat Shock Proteins.Carlomagno Y, Zhang Y, Davis M, Lin WL, Cook C, Dunmore J, Tay W, Menkosky K, Cao X, Petrucelli L, Deture MPLoS One. 2014 Mar 4;9(3):e90452. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0090452. eCollection 2014.6.Disease-Associated Mutations of TDP-43 Promote Turnover of the Protein Through the Proteasomal Pathway.Araki W, Minegishi S, Motoki K, Kume H, Hohjoh H, Araki YM, Tamaoka AMol Neurobiol. 2014 Jan 30.7.Reduced cellular Ca2+ availability enhances TDP-43 cleavage by apoptotic caspases.De Marco G, Lomartire A, Mandili G, Lupino E, Buccinna B, Ramondetti C, Moglia C, Novelli F, Piccinini M, Mostert M, Rinaudo MT, Chio A, Calvo A.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Jan 16. pii: S0167-4889(14)00014-7.8.TDP-43 Causes Differential Pathology in Neuronal versus Glial Cells in the Mouse Brain.Yan S, Wang CE, Wei W, Gaertig MA, Lai L, Li S, Li XJHum Mol Genet. 2014 Jan 10.9.Multiple organ involvement by alpha-synuclein pathology in Lewy body disorders.Gelpi E, Navarro-Otano J, Tolosa E, Gaig C, Compta Y, Rey MJ, Marti MJ, Hernandez I, Valldeoriola F, Rene R, Ribalta TMov Disord. 2014 Jul;29(8):1010-8. doi: 10.1002/mds.25776. Epub 2014 Jan 2.10.Widespread RNA metabolism impairment in sporadic inclusion body myositis TDP43-proteinopathy.Cortese A, Plagnol V, Brady S, Simone R, Lashley T, Acevedo-Arozena A, de Silva R, Greensmith L, Holton J, Hanna MG, Fisher EM, Fratta P.Neurobiol Aging. 2014 Jun;35(6):1491-8.11.Plasma phosphorylated TDP-43 levels are elevated in patients with frontotemporal dementia carrying a C9orf72 repeat expansion or a GRN mutation.Suarez-Calvet M, Dols-Icardo O, Llado A, Sanchez-Valle R, Hernandez I, Amer G, Anton-Aguirre S, Alcolea D, Fortea J, Ferrer I, van der Zee J, Dillen L, Van Broeckhoven C, Molinuevo JL, Blesa R, Clarimon J, Lleo AJ Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2013 Dec 4. doi: 10.1136/jnnp-2013-305972.12.Parkin reverses TDP-43-induced cell death and failure of amino acid homeostasis.Hebron M, Chen W, Miessau MJ, Lonskaya I, Moussa CEJ Neurochem. 2013 Dec 2. doi: 10.1111/jnc.12630.13.The novel MAPT mutation K298E: mechanisms of mutant tau toxicity, brain pathology and tau expression in induced fibroblast-derived neurons.Iovino M, Pfisterer U, Holton JL, Lashley T, Swingler RJ, Calo L, Treacy R, Revesz T, Parmar M, Goedert M, Muqit MM, Spillantini MGActa Neuropathol. 2013 Nov 30.14.Prominent psychiatric symptoms in patients with Parkinson's disease and concomitant argyrophilic grain disease.Grau-Rivera O, Gelpi E, Rey MJ, Valldeoriola F, Tolosa E, Compta Y, Marti MJJ Neurol. 2013 Sep 18.15.The long non-coding RNA nuclear-enriched abundant transcript 1_2 induces paraspeckle formation in the motor neuron during the early phase of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.Nishimoto Y, Nakagawa S, Hirose T, Okano HJ, Takao M, Shibata S, Suyama S, Kuwako K, Imai T, Murayama S, Suzuki N, Okano HMol Brain. 2013 Jul 8;6(1):31.16.Asymptomatic hyper-creatine-kinase-emia as sole manifestation of inclusion body myositis.Finsterer J, Stollberger C, Kovacs GG.Neurol Int. 2013 Jun 25;5(2):34-617.Reduced cholinergic olfactory centrifugal inputs in patients with neurodegenerative disorders and MPTP-treated monkeys.Mundinano IC, Hernandez M, Dicaudo C, Ordonez C, Marcilla I, Tunon MT, Luquin MRActa Neuropathol. 2013 Jun 20.18.Expression of ALS-linked TDP-43 mutant in astrocytes causes non-cell-autonomous motor neuron death in rats.Tong J, Huang C, Bi F, Wu Q, Huang B, Liu X, Li F, Zhou H, Xia XGEMBO J. 2013 May 28. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2013.122.19.Globular glial-like inclusions in a patient with advanced Alzheimer's disease.Gelpi E, Cullel F, Navarro-Otano J, Llado AActa Neuropathol. 2013 Jul;126(1):155-7. doi: 10.1007/s00401-013-1131-8. Epub 2013 May 23.20.Selective Forelimb Impairment in Rats Expressing a Pathological TDP-43 25?kDa C-terminal Fragment to Mimic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis.Dayton RD, Gitcho MA, Orchard EA, Wilson JD, Wang DB, Cain CD, Johnson JA, Zhang YJ, Petrucelli L, Mathis JM, Klein RLMol Ther. 2013 May 21. doi: 10.1038/mt.2013.88.21.Cell injury and premature neurodegeneration in focal malformations of cortical development.Iyer A, Prabowo A, Anink J, Spliet WG, van Rijen PC, Aronica EBrain Pathol. 2013 Apr 16. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12060.22.Neurodegenerative disease status and post-mortem pathology in idiopathic rapid-eye-movement sleep behaviour disorder: an observational cohort study.Iranzo A, Tolosa E, Gelpi E, Molinuevo JL, Valldeoriola F, Serradell M, Sanchez-Valle R, Vilaseca I, Lomena F, Vilas D, Llado A, Gaig C, Santamaria JLancet Neurol. 2013 Apr 2. pii: S1474-4422(13)70056-5. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70056-5.23.Reactive astrocytes secrete lcn2 to promote neuron death.Bi F, Huang C, Tong J, Qiu G, Huang B, Wu Q, Li F, Xu Z, Bowser R, Xia XG, Zhou HProc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Mar 5;110(10):4069-74. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1218497110. Epub 2013 Feb 19.24.Primary progressive aphasia with parkinsonism: Clinicopathological case.Doherty KM, Rohrer JD, Lees AJ, Holton JL, Warren JMov Disord. 2013 Feb 11. doi: 10.1002/mds.25341.25.Abnormal Regenerative Responses and Impaired Axonal Outgrowth after Nerve Crush in TDP-43 Transgenic Mouse Models of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis.Swarup V, Audet JN, Phaneuf D, Kriz J, Julien JP.J Neurosci. 2012 Dec 12;32(50):18186-95. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2267-12.2012.26.Parkin Ubiquitinates Tar-DNA Binding Protein-43 (TDP-43) and Promotes Its Cytosolic Accumulation via Interaction with Histone Deacetylase 6 (HDAC6).Hebron ML, Lonskaya I, Sharpe K, Weerasinghe PP, Algarzae NK, Shekoyan AR, Moussa CEJ Biol Chem. 2013 Feb 8;288(6):4103-15. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.419945. Epub 2012 Dec 20.27.Accelerated Disease Onset with Stabilized Familial Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)-linked Mutant TDP-43 Proteins.Watanabe S, Kaneko K, Yamanaka KJ Biol Chem. 2013 Feb 1;288(5):3641-54. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.433615. Epub 2012 Dec 12.28.XBP1 Depletion Precedes Ubiquitin Aggregation and Golgi Fragmentation in TDP-43 Transgenic Rats.Tong J, Huang C, Bi F, Wu Q, Huang B, Zhou H.J Neurochem. 2012 Nov;123(3):406-16. doi: 10.1111/jnc.12014.29.Characterization of Thorn-Shaped Astrocytes in White Matter of Temporal Lobe in Alzheimer's Disease Brains.Lopez-Gonzalez I, Carmona M, Blanco R, Luna-Munoz J, Martinez-Mandonado A, Mena R, Ferrer I.Brain Pathol. 2012 Aug 13. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2012.00627.x. [Epub ahead of print]30.TDP-43 plasma levels are higher in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.Verstraete E, Kuiperij HB, van Blitterswijk MM, Veldink JH, Schelhaas HJ, van den Berg LH, Verbeek MM.Amyotroph Lateral Scler. 2012 Sep;13(5):446-51. Epub 2012 Aug 8.31.MAPT H1 haplotype is associated with enhanced ?-synuclein deposition in dementia with Lewy bodies.Colom-Cadena M, Gelpi E, Marti MJ, Charif S, Dols-Icardo O, Blesa R, Clarimon J, Lleo A.Neurobiol Aging. 2012 Jul 20.32.Pick's pathology in Parkinson's disease with dementia.Vilas D, Marti MJ, Botta-Orfila T, Colom-Cadena M, Gelpi E.Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2012 Jun 12. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.2012.01287.x.33.Atypical neuropathological sCJD-MM phenotype with abundant white matter Kuru-type plaques sparing the cerebellar cortex.Gelpi E, Soler Insa JM, Parchi P, Saverioni D, Yague J, Nos C, Martinez-Saez E, Ribalta T, Ferrer I, Sanchez-Valle R.Neuropathology. 2012 Aug 6. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1789.2012.01341.x.34.Co-occurrence of Different Pathologies in Dementia: Implications for Dementia Diagnosis.Echavarri C, Burgmans S, Caballero MC, Garcia-Bragado F, Verhey FR, Uylings HB.J Alzheimers Dis. 2012 Apr 10.35.Wild Type TDP-43 Induces Neuro-Inflammation and Alters APP Metabolism in Lentiviral Gene Transfer Models.Herman AM, Khandelwal PJ, Rebeck GW, Moussa CE.Exp Neurol. 2012 Feb 28. [Epub ahead of print]36.An MND/ALS phenotype associated with C9orf72 repeat expansion: Abundant p62-positive, TDP-43-negative inclusions in cerebral cortex, hippocampus and cerebellum but without associated cognitive decline.Troakes C, Maekawa S, Wijesekera L, Rogelj B, Siklos L, Bell C, Smith B, Newhouse S, Vance C, Johnson L, Hortobagyi T, Shatunov A, Al-Chalabi A, Leigh N, Shaw CE, King A, Al-Sarraj S.Neuropathology. 2011 Dec 19. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1789.2011.01286.x.37.Mutant TDP-43 in motor neurons promotes the onset and progression of ALS in rats.Huang C, Tong J, Bi F, Zhou H, Xia XG.J Clin Invest. 2012 Jan 3;122(1):107-18. doi: 10.1172/JCI59130. Epub 2011 Dec 12.38.Frontotemporal lobar degeneration related proteins induce only subtle memory-related deficits when bilaterally overexpressed in the dorsal hippocampus.Dayton RD, Wang DB, Cain CD, Schrott LM, Ramirez JJ, King MA, Klein RL.Exp Neurol. 2011 Dec 9.39.TDP-43 regulates global translational yield by splicing of exon junction complex component SKAR.Fiesel FC, Weber SS, Supper J, Zell A, Kahle PJ.Nucleic Acids Res. 2011 Nov 25.40.Epitope mapping of antibodies against TDP-43 and detection of protease-resistant fragments of pathological TDP-43 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and frontotemporal lobar degeneration.Tsuji H, Nonaka T, Yamashita M, Suzukake M, Kametani F, Akiyama H, Mann DM, Tamaoka A, Hasegawa M.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011 Nov 22.41.Breakpoint Sequence Analysis of an A?]PP Locus Duplication Associated with Autosomal Dominant Alzheimer's Disease and Severe Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy.Antonell A, Gelpi E, Sanchez-Valle R, Martinez R, Molinuevo JL, Llado A.J Alzheimers Dis. 2011 Oct 18.42.Neurofibrillary tangle pathology and Braak staging in chronic epilepsy in relation to traumatic brain injury and hippocampal sclerosis: a post-mortem study.Thom M, Liu JY, Thompson P, Phadke R, Narkiewicz M, Martinian L, Marsdon D, Koepp M, Caboclo L, Catarino CB, Sisodiya SM.Brain. 2011 Oct;134(Pt 10):2969-81. Epub 2011 Sep 8.43.The ALS-associated proteins FUS and TDP-43 function together to affect Drosophila locomotion and life span.Wang JW, Brent JR, Tomlinson A, Shneider NA, McCabe BD.J Clin Invest. 2011 Sep 1. pii: 57883. doi: 10.1172/JCI57883. [Epub ahead of print]44.Pathological hallmarks of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/frontotemporal lobar degeneration in transgenic mice produced with TDP-43 genomic fragments.Swarup V, Phaneuf D, Bareil C, Robertson J, Rouleau GA, Kriz J, Julien JP.Brain. 2011 Jul 13. [Epub ahead of print]45.Hirano body - rich subtypes of Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease.Martinez-Saez E, Gelpi E, Rey M, Ferrer I, Ribalta T, Botta-Orfila T, Nos C, Yague J, Sanchez-Valle R.Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2011 Jul 5. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2990.2011.01208.x.46.Identification of c-myc-dependent proteins in the medulloblastoma cell line D425Med.Azizi AA, Li L, Strobel T, Chen WQ, Slavc I, Lubec G.Amino Acids. 2011 Jun 12. [Epub ahead of print]47.Molecular mechanisms of MLC1 and GLIALCAM mutations in megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts.Lopez-Hernandez T, Sirisi S, Capdevila-Nortes X, Montolio M, Fernandez-Duenas V, Scheper GC, van der Knaap MS, Casquero P, Ciruela F, Ferrer I, Nunes V, Estevez R.Hum Mol Genet. 2011 Jun 7. [Epub ahead of print]48.FTLD-TDP with motor neuron disease, visuospatial impairment and a progressive supranuclear palsy-like syndrome: broadening the clinical phenotype of TDP-43 proteinopathies. A report of three cases.Rusina R, Kovacs GG, Fiala J, Hort J, Ridzon P, Holmerova I, Strobel T, Matej R.BMC Neurol. 2011 May 10;11:50.49.Increased dopaminergic cells and protein aggregates in the olfactory bulb of patients with neurodegenerative disorders.Mundinano IC, Caballero MC, Ordonez C, Hernandez M, Dicaudo C, Marcilla I, Erro ME, Tunon MT, Luquin MR.Acta Neuropathol. 2011 May 8. [Epub ahead of print]50.Distribution and Pattern of Pathology in Subjects with Familial or Sporadic Late-Onset Cerebellar Ataxia as Assessed by p62/Sequestosome Immunohistochemistry.Pikkarainen M, Hartikainen P, Soininen H, Alafuzoff I.Cerebellum. 2011 May 5. [Epub ahead of print]51.Unusual clinical presentation and neuropathology in two subjects with fused-in sarcoma (FUS) positive inclusions.Hartikainen PH, Pikkarainen M, Hanninen T, Soininen H, Alafuzoff I.Neuropathology. 2011 Apr 26. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1789.2011.01218.x. [Epub ahead of print]52.Aggregation of the 35-kDa fragment of TDP-43 causes formation of cytoplasmic inclusions and alteration of RNA processing.Che MX, Jiang YJ, Xie YY, Jiang LL, Hu HY.FASEB J. 2011 Apr 8. [Epub ahead of print]53.TDP-43 Potentiates Alpha-synuclein Toxicity to Dopaminergic Neurons in Transgenic Mice.Tian T, Huang C, Tong J, Yang M, Zhou H, Xia XG.Int J Biol Sci. 2011 Mar 4;7(2):234-43.54.Beta-amyloid triggers ALS-associated TDP-43 pathology in AD models.Herman AM, Khandelwal PJ, Stanczyk BB, Rebeck GW, Moussa CE.Brain Res. 2011 Mar 1. [Epub ahead of print]55.TDP-43 pathology may occur in the BRI2 gene-related dementias.Lashley T, Holton JL, Revesz T.Acta Neuropathol. 2011 Feb 22. [Epub ahead of print]56.TAR-DNA binding protein-43 and alterations in the hippocampus.Rauramaa T, Pikkarainen M, Englund E, Ince PG, Jellinger K, Paetau A, Alafuzoff I.J Neural Transm. 2011 Jan 6. [Epub ahead of print]57.Cytoplasmic accumulation of TDP-43 in circulating lymphomonocytes of ALS patients with and without TARDBP mutations.De Marco G, Lupino E, Calvo A, Moglia C, Buccinna B, Grifoni S, Ramondetti C, Lomartire A, Rinaudo MT, Piccinini M, Giordana MT, Chio A.Acta Neuropathol. 2010 Dec 1. [Epub ahead of print]58.Tubulin polymerization promoting protein (TPPP/p25) as a marker for oligodendroglial changes in multiple sclerosis.Hoftberger R, Fink S, Aboul-Enein F, Botond G, Olah J, Berki T, Ovadi J, Lassmann H, Budka H, Kovacs GG.Glia. 2010 Nov 15;58(15):1847-57.59.TDP-43 physically interacts with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-linked mutant CuZn superoxide dismutase.Higashi S, Tsuchiya Y, Araki T, Wada K, Kabuta T.Neurochem Int. 2010 Oct 5. [Epub ahead of print]60.Expansive Gene Transfer in the Rat CNS Rapidly Produces Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Relevant Sequelae When TDP-43 is Overexpressed.Wang DB, Dayton RD, Henning PP, Cain CD, Zhao LR, Schrott LM, Orchard EA, Knight DS, Klein RL.Mol Ther. 2010 Sep 28. [Epub ahead of print]61.Wild-type human TDP-43 expression causes TDP-43 phosphorylation, mitochondrial aggregation, motor deficits, and early mortality in transgenic mice.Xu YF, Gendron TF, Zhang YJ, Lin WL, D'Alton S, Sheng H, Casey MC, Tong J, Knight J, Yu X, Rademakers R, Boylan K, Hutton M, McGowan E, Dickson DW, Lewis J, Petrucelli L.J Neurosci. 2010 Aug 11;30(32):10851-9.62.ALS-associated mutations in TDP-43 increase its stability and promote TDP-43 complexes with FUS/TLS.Ling SC, Albuquerque CP, Han JS, Lagier-Tourenne C, Tokunaga S, Zhou H, Cleveland DW.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Jul 12. [Epub ahead of print]63.Neurotoxic effects of TDP-43 overexpression in C. elegans.Ash PE, Zhang YJ, Roberts CM, Saldi T, Hutter H, Buratti E, Petrucelli L, Link CD.Hum Mol Genet. 2010 Jun 21. [Epub ahead of print]64.The first case of protease-sensitive prionopathy (PSPr) in The Netherlands: a patient with an unusual GSS-like clinical phenotype.Jansen C, Head MW, van Gool WA, Baas F, Yull H, Ironside JW, Rozemuller AJ.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2010 Jun 14. [Epub ahead of print]65.Mutations of optineurin in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.Maruyama H, Morino H, Ito H, Izumi Y, Kato H, Watanabe Y, Kinoshita Y, Kamada M, Nodera H, Suzuki H, Komure O, Matsuura S, Kobatake K, Morimoto N, Abe K, Suzuki N, Aoki M, Kawata A, Hirai T, Kato T, Ogasawara K, Hirano A, Takumi T, Kusaka H, Hagiwara K, Kaji R, Kawakami H.Nature. 2010 May 13;465(7295):223-6. Epub 2010 Apr 28.66.Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: dash-like accumulation of phosphorylated TDP-43 in somatodendritic and axonal compartments of somatomotor neurons of the lower brainstem and spinal cord.Braak H, Ludolph A, Thal DR, Del Tredici K.Acta Neuropathol. 2010 Apr 9. [Epub ahead of print]67.TDP-43 transgenic mice develop spastic paralysis and neuronal inclusions characteristic of ALS and frontotemporal lobar degeneration.Wils H, Kleinberger G, Janssens J, Pereson S, Joris G, Cuijt I, Smits V, Ceuterick-de Groote C, Van Broeckhoven C, Kumar-Singh S.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Feb 23;107(8):3858-63. Epub 2010 Feb 3.68.Depletion of oxidative and endoplasmic reticulum stress regulators in Pick disease.Ilieva EV, Naudi A, Kichev A, Ferrer I, Pamplona R, Portero-Otin M.Free Radic Biol Med. 2010 Feb 20. [Epub ahead of print]69.Alteration of biochemical and pathological properties of TDP-43 protein by a lipid mediator, 15-deoxy-Delta(12,14)-prostaglandin J(2).Zhang HX, Tanji K, Yoshida H, Hayakari M, Shibata T, Mori F, Uchida K, Wakabayashi K.Exp Neurol. 2010 Jan 18. [Epub ahead of print]70.Knockdown of transactive response DNA-binding protein (TDP-43) downregulates histone deacetylase 6.Fiesel FC, Voigt A, Weber SS, Van den Haute C, Waldenmaier A, Gorner K, Walter M, Anderson ML, Kern JV, Rasse TM, Schmidt T, Springer W, Kirchner R, Bonin M, Neumann M, Baekelandt V, Alunni-Fabbroni M, Schulz JB, Kahle PJ.EMBO J. 2010 Jan 6;29(1):209-21. Epub 2009 Nov 12.71.Characterization of alternative isoforms and inclusion body of the TAR DNA-binding protein-43.Nishimoto Y, Ito D, Yagi T, Nihei Y, Tsunoda Y, Suzuki N.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jan 1;285(1):608-19. Epub 2009 Nov 3.72.Plasma phosphorylated-TDP-43 protein levels correlate with brain pathology in frontotemporal lobar degeneration.Foulds PG, Davidson Y, Mishra M, Hobson DJ, Humphreys KM, Taylor M, Johnson N, Weintraub S, Akiyama H, Arai T, Hasegawa M, Bigio EH, Benson FE, Allsop D, Mann DM.Acta Neuropathol. 2009 Oct 13. [Epub ahead of print]73.Abnormal hippocampal distribution of TDP-43 in patients with-late onset psychosis.Velakoulis D, Walterfang M, Mocellin R, Pantelis C, Dean B, McLean C.Aust N Z J Psychiatry. 2009 Aug;43(8):739-45.74.Cytosolic TDP-43 expression following axotomy is associated with caspase 3 activation in NFL(-/-) mice: Support for a role for TDP-43 in the physiological response to neuronal injury.Moisse K, Mepham J, Volkening K, Welch I, Hill T, Strong MJ.Brain Res. 2009 Nov 3;1296:176-86. Epub 2009 Jul 18.75.Frontotemporal dementia presenting as schizophrenia-like psychosis in young people: clinicopathological series and review of cases.Velakoulis D, Walterfang M, Mocellin R, Pantelis C, McLean C.Br J Psychiatry. 2009 Apr;194(4):298-305.76.The complement factor C5a receptor is upregulated in NFL-/- mouse motor neurons.Humayun S, Gohar M, Volkening K, Moisse K, Leystra-Lantz C, Mepham J, McLean J, Strong MJ.J Neuroimmunol. 2009 May 29;210(1-2):52-62. Epub 2009 Mar 16.77.TAR DNA-Binding Protein 43 Accumulation in Protein Aggregate Myopathies.Olive M, Janue A, Moreno D, Gamez J, Torrejon-Escribano B, Ferrer I.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2009 Mar;68(3):262-73.78.VCP mutations causing frontotemporal lobar degeneration disrupt localization of TDP-43 and induce cell deathGitcho MA, Strider J, Carter D, Taylor-Reinwald L, Forman MS, Goate AM, Cairns NJ.J Biol Chem. 2009 May 1;284(18):12384-98. Epub 2009 Feb 23.79.Ubiquitin associated protein 1 is a risk factor for frontotemporal lobar degeneration.Rollinson S, Rizzu P, Sikkink S, Baker M, Halliwell N, Snowden J, Traynor BJ, Ruano D, Cairns N, Rohrer JD, Mead S, Collinge J, Rossor M, Akay E, Guerreiro R, Rademakers R, Morrison KE, Pastor P, Alonso E, Martinez-Lage P, Graff-Radford N, Neary D, HeutinNeurobiol Aging. 2009 Apr;30(4):656-65. Epub 2009 Feb 12.80.Frontotemporal dementia in a large Swedish family is caused by a progranulin null mutation.Skoglund L, Brundin R, Olofsson T, Kalimo H, Ingvast S, Blom ES, Giedraitis V, Ingelsson M, Lannfelt L, Basun H, Glaser A.Neurogenetics. 2009 Feb;10(1):27-34. Epub 2008 Oct 15.81.Expression Of TDP-43 C-terminal fragments in vitro recapitulates pathological features of TDP-43 proteinopathies.Igaz LM, Kwong LK, Chen-Plotkin A, Winton MJ, Unger TL, Xu Y, Neumann M, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM.J Biol Chem. 2009 Mar 27;284(13):8516-24. Epub 2009 Jan 21.82.Early-Onset Familial Lewy Body Dementia With Extensive Tauopathy: A Clinical, Genetic, and Neuropathological Study.Clarimon J, Molina-Porcel L, Gomez-Isla T, Blesa R, Guardia-Laguarta C, Gonzalez-Neira A, Estorch M, Ma Grau J, Barraquer L, Roig C, Ferrer I, Lleo A.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2009 Jan;68(1):73-82.83.Sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis of long duration is associated with relatively mild TDP-43 pathology.Nishihira Y, Tan CF, Hoshi Y, Iwanaga K, Yamada M, Kawachi I, Tsujihata M, Hozumi I, Morita T, Onodera O, Nishizawa M, Kakita A, Takahashi H.Acta Neuropathol. 2009 Jan;117(1):45-53. Epub 2008 Oct 16.84.Molecular pathogenesis of frontotemporal lobar degeneration: basic science seminar in neurology.Sleegers K, Kumar-Singh S, Cruts M, Van Broeckhoven C.Arch Neurol. 2008 Jun;65(6):700-4.85.Colocalization of Transactivation-Responsive DNA-Binding Protein 43 and Huntingtin in Inclusions of Huntington Disease.Schwab C, Arai T, Hasegawa M, Yu S, McGeer PL.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2008 Dec;67(12):1159-65.86.Enduring involvement of tau, beta-amyloid, alpha-synuclein, ubiquitin and TDP-43 pathology in the amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/parkinsonism-dementia complex of Guam (ALS/PDC).Miklossy J, Steele JC, Yu S, McCall S, Sandberg G, McGeer EG, McGeer PL.Acta Neuropathol. 2008 Dec;116(6):625-37. Epub 2008 Oct 9.87.Increased TDP-43 protein in cerebrospinal fluid of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.Kasai T, Tokuda T, Ishigami N, Sasayama H, Foulds P, Mitchell DJ, Mann DM, Allsop D, Nakagawa M.Acta Neuropathol. 2009 Jan;117(1):55-62. Epub 2008 Nov 7.88.TDP-43 in Cerebrospinal Fluid of Patients With Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis.Steinacker P, Hendrich C, Sperfeld AD, Jesse S, von Arnim CA, Lehnert S, Pabst A, Uttner I, Tumani H, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Kretzschmar HA, Ludolph A, Neumann M, Otto M.Arch Neurol. 2008 Nov;65(11):1481-7.89.Expression of collagen XVII and ubiquitin-binding protein p62 in motor neuron disease.Seppanen A, Pikkarainen M, Hartikainen P, Hofmann SC, Majamaa K, Alafuzoff I.Brain Res. 2009 Jan 9;1247:171-7. Epub 2008 Nov 1.90.TDP-43 accumulation in inclusion body myopathy muscle suggests a common pathogenic mechanism with frontotemporal dementia.Weihl CC, Temiz P, Miller SE, Watts G, Smith C, Forman M, Hanson PI, Kimonis V, Pestronk A.J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2008 Oct;79(10):1186-9.91.Divergent patterns of cytosolic TDP-43 and neuronal progranulin expression following axotomy: Implications for TDP-43 in the physiological response to neuronal injury.Moisse K, Volkening K, Leystra-Lantz C, Welch I, Hill T, Strong MJ.Brain Research (2008), doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2008.10.02192.White Matter Tauopathy With Globular Glial Inclusions: A Distinct Sporadic Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration.Kovacs GG, Majtenyi K, Spina S, Murrell JR, Gelpi E, Hoftberger R, Fraser G, Crowther RA, Goedert M, Budka H, Ghetti B.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2008 Oct;67(10):963-75.93.Ultrastructural localization of TDP-43 in filamentous neuronal inclusions in various neurodegenerative diseases.Lin WL, Dickson DW.Acta Neuropathol. 2008 Aug;116(2):205-13. Epub 2008 Jul 8.94.Maturation process of TDP-43-positive neuronal cytoplasmic inclusions in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with and without dementia.Mori F, Tanji K, Zhang HX, Nishihira Y, Tan CF, Takahashi H, Wakabayashi K.Acta Neuropathol. 2008 Aug;116(2):193-203. Epub 2008 Jun 17.95.Enrichment of C-Terminal Fragments in TAR DNA-Binding Protein-43 Cytoplasmic Inclusions in Brain but not in Spinal Cord of Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis.Igaz LM, Kwong LK, Xu Y, Truax AC, Uryu K, Neumann M, Clark CM, Elman LB, Miller BL, Grossman M, McCluskey LF, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM.Am J Pathol. 2008 Jul;173(1):182-94. Epub 2008 Jun 5.96.TDP-43 protein in plasma may index TDP-43 brain pathology in Alzheimer's disease and frontotemporal lobar degeneration.Foulds P, McAuley E, Gibbons L, Davidson Y, Pickering-Brown SM, Neary D, Snowden JS, Allsop D, Mann DM.Acta Neuropathol. 2008 Aug;116(2):141-6. Epub 2008 May 28.97.A yeast TDP-43 proteinopathy model: Exploring the molecular determinants of TDP-43 aggregation and cellular toxicity.Johnson BS, McCaffery JM, Lindquist S, Gitler AD.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Apr 29;105(17):6439-44. Epub 2008 Apr 23.98.A distinct clinical, neuropsychological and radiological phenotype is associated with progranulin gene mutations in a large UK series.Beck J, Rohrer JD, Campbell T, Isaacs A, Morrison KE, Goodall EF, Warrington EK, Stevens J, Revesz T, Holton J, Al-Sarraj S, King A, Scahill R, Warren JD, Fox NC, Rossor MN, Collinge J, Mead S.Brain. 2008 Mar;131(Pt 3):706-20. Epub 2008 Jan 29.99.Disturbance of nuclear and cytoplasmic Tar DNA binding protein (TDP-43) induces disease-like redistribution, sequestration and aggregate formation.Winton MJ, Igaz LM, Wong MM, Kwong LK, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM.J Biol Chem. 2008 May 9;283(19):13302-9. Epub 2008 Feb 27.100.Epitope mapping of 2E2-D3, a monoclonal antibody directed against human TDP-43.Zhang HX, Tanji K, Mori F, Wakabayashi K.Neurosci Lett. 2008 Mar 28;434(2):170-4. Epub 2008 Feb 2.101.Missense mutations in the progranulin gene linked to frontotemporal lobar degeneration with ubiquitin-immunoreactive inclusions reduce progranulin production and secretion.Shankaran SS, Capell A, Hruscha AT, Fellerer K, Neumann M, Schmid B, Haass C.J Biol Chem. 2008 Jan 18;283(3):1744-53. Epub 2007 Nov 5.102.MAPT S305I mutation: implications for argyrophilic grain disease.Kovacs GG, Pittman A, Revesz T, Luk C, Lees A, Kiss E, Tariska P, Laszlo L, Molnar K, Molnar MJ, Tolnay M, de Silva R.Acta Neuropathol. 2008 Jul;116(1):103-18. Epub 2007 Dec 8.103.Evidence That TDP-43 is Not the Major Ubiquitinated Target Within the Pathological Inclusions of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis.Sanelli T, Xiao S, Horne P, Bilbao J, Zinman L, Robertson J.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2007 Dec;66(12):1147-53.104.FTLD-U linked missense mutations in the progranulin gene reduce progranulin production and secretion.Shankaran SS, Capell A, Hruscha AT, Fellerer K, Neumann M, Schmid B, Haass C.J. Biol. Chem, 10.1074/jbc.M705115200105.TDP-43-immunoreactive neuronal and glial inclusions in the neostriatum in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with and without dementia.Zhang H, Tan CF, Mori F, Tanji K, Kakita A, Takahashi H, Wakabayashi K.Acta Neuropathol. 2008 Jan;115(1):115-22. Epub 2007 Sep 5.106.TDP-43 immunoreactivity in hippocampal sclerosis and Alzheimer's disease.Amador-Ortiz C, Lin WL, Ahmed Z, Personett D, Davies P, Duara R, Graff-Radford NR, Hutton ML, Dickson DW.Ann Neurol. 2007 May;61(5):435-45.107.Pathological TDP-43 distinguishes sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis from amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with SOD1 mutations.Mackenzie IR, Bigio EH, Ince PG, Geser F, Neumann M, Cairns NJ, Kwong LK, Forman MS, Ravits J, Stewart H, Eisen A, McClusky L, Kretzschmar HA, Monoranu CM, Highley JR, Kirby J, Siddique T, Shaw PJ, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ.Ann Neurol. 2007 May;61(5):427-34.108.TDP-43 immunoreactivity in neuronal inclusions in familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis with or without SOD1 gene mutation.Tan CF, Eguchi H, Tagawa A, Onodera O, Iwasaki T, Tsujino A, Nishizawa M, Kakita A, Takahashi H.Acta Neuropathol (Berl). 2007 May;113(5):535-42. Epub 2007 Feb 27.109.DEAD-box RNA helicase subunits of the Drosha complex are required for processing of rRNA and a subset of microRNAs.Fukuda T, Yamagata K, Fujiyama S, Matsumoto T, Koshida I, Yoshimura K, Mihara M, Naitou M, Endoh H, Nakamura T, Akimoto C, Yamamoto Y, Katagiri T, Foulds C, Takezawa S, Kitagawa H, Takeyama K, O'Malley BW, Kato S.Nat Cell Biol. 2007 May;9(5):604-11. Epub 2007 Apr 15.110.TDP-43 is deposited in the Guam parkinsonism-dementia complex brains.Hasegawa M, Arai T, Akiyama H, Nonaka T, Mori H, Hashimoto T, Yamazaki M, Oyanagi K.Brain. 2007 May;130(Pt 5):1386-94. Epub 2007 Apr 17.111.TDP-43-positive white matter pathology in frontotemporal lobar degeneration with ubiquitin-positive inclusions.Neumann M, Kwong LK, Truax AC, Vanmassenhove B, Kretzschmar HA, Van Deerlin VM, Clark CM, Grossman M, Miller BL, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2007 Mar;66(3):177-83.112.TDP-43 in the ubiquitin pathology of frontotemporal dementia with VCP gene mutations.Neumann M, Mackenzie IR, Cairns NJ, Boyer PJ, Markesbery WR, Smith CD, Taylor JP, Kretzschmar HA, Kimonis VE, Forman MS.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2007 Feb;66(2):152-7.113.TDP-43 is a component of ubiquitin-positive tau-negative inclusions in frontotemporal lobar degeneration and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.Arai T, Hasegawa M, Akiyama H, Ikeda K, Nonaka T, Mori H, Mann D, Tsuchiya K, Yoshida M, Hashizume Y, Oda T.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006 Dec 22;351(3):602-11. Epub 2006 Oct 30.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.











 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.