SMC1A Antibody (N-term) Blocking peptide
Synthetic peptide
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND
| Primary Accession | Q14683 |
|---|---|
| Clone Names | 100427098 |
| Gene ID | 8243 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Structural maintenance of chromosomes protein 1A, SMC protein 1A, SMC-1-alpha, SMC-1A, Sb18, SMC1A, DXS423E, KIAA0178, SB18, SMC1, SMC1L1 |
| Target/Specificity | The synthetic peptide sequence used to generate the antibody AP13544a was selected from the N-term region of SMC1A. A 10 to 100 fold molar excess to antibody is recommended. Precise conditions should be optimized for a particular assay. |
| Format | Peptides are lyophilized in a solid powder format. Peptides can be reconstituted in solution using the appropriate buffer as needed. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 6 months. For long term storage store at -20°C. |
| Precautions | This product is for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | SMC1A |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | DXS423E, KIAA0178, SB1.8, SMC1, SMC1L1 |
| Function | Involved in chromosome cohesion during cell cycle and in DNA repair. Central component of cohesin complex. The cohesin complex is required for the cohesion of sister chromatids after DNA replication. The cohesin complex apparently forms a large proteinaceous ring within which sister chromatids can be trapped. At anaphase, the complex is cleaved and dissociates from chromatin, allowing sister chromatids to segregate. The cohesin complex may also play a role in spindle pole assembly during mitosis. Involved in DNA repair via its interaction with BRCA1 and its related phosphorylation by ATM, or via its phosphorylation by ATR. Works as a downstream effector both in the ATM/NBS1 branch and in the ATR/MSH2 branch of S-phase checkpoint. |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus. Chromosome. Chromosome, centromere, kinetochore. Note=Associates with chromatin. Before prophase it is scattered along chromosome arms. During prophase, most of cohesin complexes dissociate from chromatin probably because of phosphorylation by PLK, except at centromeres, where cohesin complexes remain. At anaphase, the RAD21 subunit of the cohesin complex is cleaved, leading to the dissociation of the complex from chromosomes, allowing chromosome separation. In germ cells, cohesin complex dissociates from chromatin at prophase I, and may be replaced by a meiosis-specific cohesin complex. The phosphorylated form on Ser-957 and Ser-966 associates with chromatin during G1/S/G2 phases but not during M phase, suggesting that phosphorylation does not regulate cohesin function. Integral component of the functional centromere- kinetochore complex at the kinetochore region during mitosis |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Proper cohesion of sister chromatids is a prerequisite forthe correct segregation of chromosomes during cell division. Thecohesin multiprotein complex is required for sister chromatidcohesion. This complex is composed partly of two structuralmaintenance of chromosomes (SMC) proteins, SMC3 and either SMC1L2or the protein encoded by this gene. Most of the cohesin complexesdissociate from the chromosomes before mitosis, although thosecomplexes at the kinetochore remain. Therefore, the encoded proteinis thought to be an important part of functional kinetochores. Inaddition, this protein interacts with BRCA1 and is phosphorylatedby ATM, indicating a potential role for this protein in DNA repair.This gene, which belongs to the SMC gene family, is located in anarea of the X-chromosome that escapes X inactivation. [provided byRefSeq].
References
Limongelli, G., et al. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 152A (8), 2127-2129 (2010) :Homme, C., et al. Oncol. Rep. 24(1):47-56(2010)Pie, J., et al. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 152A (4), 924-929 (2010) :Wong, R.W. Cell Cycle 9(1):198-200(2010)Liu, J., et al. Hum. Mutat. 30(11):1535-1542(2009)
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.




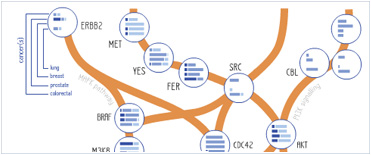







 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.

