ZFP36L1 Blocking Peptide(N-term)
Synthetic peptide
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND
| Primary Accession | Q07352 |
|---|---|
| Other Accession | P17431, P23950, NP_004917.2 |
| Gene ID | 677 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Zinc finger protein 36, C3H1 type-like 1, Butyrate response factor 1, EGF-response factor 1, ERF-1, Protein TIS11B, ZFP36L1, BERG36, BRF1, ERF1, RNF162B, TIS11B |
| Target/Specificity | The synthetic peptide sequence is selected from aa 79-93 of HUMAN ZFP36L1 |
| Format | Peptides are lyophilized in a solid powder format. Peptides can be reconstituted in solution using the appropriate buffer as needed. |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 6 months. For long term storage store at -20°C. |
| Precautions | This product is for research use only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | ZFP36L1 (HGNC:1107) |
|---|---|
| Function | Zinc-finger RNA-binding protein that destabilizes several cytoplasmic AU-rich element (ARE)-containing mRNA transcripts by promoting their poly(A) tail removal or deadenylation, and hence provide a mechanism for attenuating protein synthesis (PubMed:12198173, PubMed:15538381, PubMed:15467755, PubMed:17030608, PubMed:19179481, PubMed:20702587, PubMed:24700863, PubMed:25106868, PubMed:25014217, PubMed:26542173). Acts as a 3'-untranslated region (UTR) ARE mRNA- binding adapter protein to communicate signaling events to the mRNA decay machinery (PubMed:15687258). Functions by recruiting the CCR4-NOT deadenylase complex and components of the cytoplasmic RNA decay machinery to the bound ARE-containing mRNAs, and hence promotes ARE- mediated mRNA deadenylation and decay processes (PubMed:15687258, PubMed:18326031, PubMed:25106868). Induces also the degradation of ARE- containing mRNAs even in absence of poly(A) tail (By similarity). Binds to 3'-UTR ARE of numerous mRNAs (PubMed:12198173, PubMed:15538381, PubMed:15467755, PubMed:17030608, PubMed:19179481, PubMed:20702587, PubMed:24700863, PubMed:25106868, PubMed:25014217, PubMed:26542173). Positively regulates early adipogenesis by promoting ARE-mediated mRNA decay of immediate early genes (IEGs) (By similarity). Promotes ARE- mediated mRNA decay of mineralocorticoid receptor NR3C2 mRNA in response to hypertonic stress (PubMed:24700863). Negatively regulates hematopoietic/erythroid cell differentiation by promoting ARE-mediated mRNA decay of the transcription factor STAT5B mRNA (PubMed:20702587). Positively regulates monocyte/macrophage cell differentiation by promoting ARE-mediated mRNA decay of the cyclin-dependent kinase CDK6 mRNA (PubMed:26542173). Promotes degradation of ARE-containing pluripotency-associated mRNAs in embryonic stem cells (ESCs), such as NANOG, through a fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-induced MAPK-dependent signaling pathway, and hence attenuates ESC self-renewal and positively regulates mesendoderm differentiation (By similarity). May play a role in mediating pro-apoptotic effects in malignant B-cells by promoting ARE-mediated mRNA decay of BCL2 mRNA (PubMed:25014217). In association with ZFP36L2 maintains quiescence on developing B lymphocytes by promoting ARE-mediated decay of several mRNAs encoding cell cycle regulators that help B cells progress through the cell cycle, and hence ensuring accurate variable-diversity-joining (VDJ) recombination and functional immune cell formation (By similarity). Together with ZFP36L2 is also necessary for thymocyte development and prevention of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (T-ALL) transformation by promoting ARE- mediated mRNA decay of the oncogenic transcription factor NOTCH1 mRNA (By similarity). Participates in the delivery of target ARE-mRNAs to processing bodies (PBs) (PubMed:17369404). In addition to its cytosolic mRNA-decay function, plays a role in the regulation of nuclear mRNA 3'- end processing; modulates mRNA 3'-end maturation efficiency of the DLL4 mRNA through binding with an ARE embedded in a weak noncanonical polyadenylation (poly(A)) signal in endothelial cells (PubMed:21832157). Also involved in the regulation of stress granule (SG) and P-body (PB) formation and fusion (PubMed:15967811). Plays a role in vasculogenesis and endocardial development (By similarity). Plays a role in the regulation of keratinocyte proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis (PubMed:27182009). Plays a role in myoblast cell differentiation (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus. Cytoplasm. Cytoplasmic granule. Cytoplasm, P-body Note=Shuttles between the nucleus and the cytoplasm in a XPO1/CRM1- dependent manner (By similarity). Component of cytoplasmic stress granules (PubMed:15967811). Localizes in processing bodies (PBs) (PubMed:17369404). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:P23950, ECO:0000269|PubMed:15967811, ECO:0000269|PubMed:17369404} |
| Tissue Location | Expressed mainly in the basal epidermal layer, weakly in the suprabasal epidermal layers (PubMed:27182009). Expressed in epidermal keratinocytes (at protein level) (PubMed:27182009) Expressed in osteoblasts (PubMed:15465005) |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
This gene is a member of the TIS11 family of early response genes. Family members are induced by various agonists such as the phorbol ester TPA and the polypeptide mitogen EGF. The gene is well conserved across species and has a promoter that contains motifs seen in other early-response genes. The encoded protein contains a distinguishing putative zinc finger domain with a repeating cys-his motif. This putative nuclear transcription factor most likely functions in regulating the response to growth factors.
References
Hacker, C., et al. Growth Factors 28(3):178-190(2010)
Dubois, P.C., et al. Nat. Genet. 42(4):295-302(2010)
Sinha, S., et al. J. Biol. Chem. 284(47):32610-32618(2009)
Cheng, Z., et al. Genes Dev. 23(9):1106-1118(2009)
Baou, M., et al. Leukemia 23(5):986-989(2009)
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.




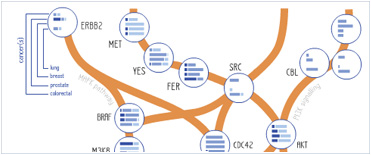







 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.

