PKAca, Active recombinant protein
PKA, cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND
| Primary Accession | P17612 |
|---|---|
| Concentration | 0.1 |
| Calculated MW | 69.0 kDa |
| Gene ID | 5566 |
|---|---|
| Gene Symbol | PRKACA |
| Other Names | PKA, cAMP-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha |
| Source | Baculovirus (Sf9 insect cells) |
| Assay&Purity | SDS-PAGE; ≥90% |
| Assay2&Purity2 | HPLC; |
| Recombinant | Yes |
| Format | Liquid |
| Storage | -80°C; Recombinant proteins in storage buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 0.25 mM DTT, 0.1 mM EGTA, 0.1 mM EDTA, 0.1 mM PMSF, 25% glycerol). |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
Most of the effects of cAMP are mediated through the phosphorylation of target proteins on serine or threonine residues by the cAMP-dependent protein kinase (AMPK). The inactive holoenzyme of AMPK is a tetramer composed of two regulatory and two catalytic subunits. The mammalian catalytic subunit has been shown to consist of three PKA gene products: C-α, C-β, and C-γ. Two PKA isoforms exist, designated types I and II, which differ in their dimeric regulatory subunits, designated RI and RII, respectively. Furthermore, there are at least four different regulatory subunits: RI-α, RI-β, RII-α, and RII-β. cAMP causes the dissociation of the inactive holoenzyme into a dimer of regulatory subunits bound to four cAMP and two free monomeric catalytic subunits. The catalytic subunit C-α of PKA (PKAca) is a member of the Ser/Thr protein kinase family and is a catalytic subunit C-β of AMPK. Tasken et al. assigned the PKAca gene to 19p13.1 (1). Yasuda et al found that protein kinase A is required for long-term potentiation in neonatal tissue and suggested that developmental changes in synapse morphology may underlie the changes in the kinase activity (2). Skalhegg et al generated a null mutation in the major catalytic subunit of PKAca, and observed early postnatal lethality in the majority of C-α knockout mice. Surprisingly, a small percentage of C-α knockout mice, although runted, survived to adulthood. In these animals, compensatory increases in C-β levels occurred in brain whereas many tissues, including skeletal muscle, heart, and sperm, contained less than 10% of the normal PKA activity (3).
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.




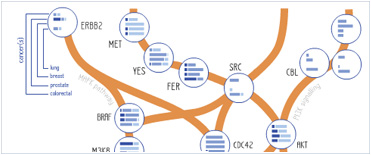







 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.

