Anti-Aurora A Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P97477 |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Reactivity | Mouse, Rat |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Format | Lyophilized |
| Description | Rabbit IgG polyclonal antibody for Aurora kinase A(AURKA) detection. Tested with WB in Mouse;Rat. |
| Reconstitution | Add 0.2ml of distilled water will yield a concentration of 500ug/ml. |
| Gene ID | 20878 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Aurora kinase A, 2.7.11.1, Aurora 2, Aurora family kinase 1, Aurora/IPL1-related kinase 1, ARK-1, Aurora-related kinase 1, Ipl1- and aurora-related kinase 1, Serine/threonine-protein kinase 6, Serine/threonine-protein kinase Ayk1, Serine/threonine-protein kinase aurora-A, Aurka |
| Calculated MW | 44772 MW KDa |
| Application Details | Western blot, 0.1-0.5 µg/ml, Mouse, Rat |
| Subcellular Localization | Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, spindle pole. Localizes on centrosomes in interphase cells and at each spindle pole in mitosis. Associates with both the pericentriolar material (PCM) and centrioles. Colocalized with SIRT2 at centrosome (By similarity). Detected at the neurite hillock in developing neurons. . |
| Tissue Specificity | Detected in embryonic neurons in dorsal root ganglia and brain cortex (at protein level). Highly expressed in testis, in about one third of the seminiferous tubules. Expression is restricted to specific spermatocytes nearing completion of prophase, with levels falling off on transition to elongated spermatids. Highly expressed in the ovary, expression in the oocyte starts around the transition to large growing follicle. Abundant expression is seen in the proliferating granulosa and thecal cells of the growing follicle, and in the young corpus luteum. Very weakly expressed in spleen and intestine. . |
| Protein Name | Aurora kinase A |
| Contents | Each vial contains 5mg BSA, 0.9mg NaCl, 0.2mg Na2HPO4, 0.05mg Thimerosal, 0.05mg NaN3. |
| Immunogen | A synthetic peptide corresponding to a sequence in the middle region of mouse Aurora A(109-125aa QKTEDTKKRQWTLEDFD), different from the related rat sequence by one amino acid. |
| Purification | Immunogen affinity purified. |
| Cross Reactivity | No cross reactivity with otherproteins |
| Storage | At -20˚C for one year. After r˚Constitution, at 4˚C for one month. It˚Can also be aliquotted and stored frozen at -20˚C for a longer time.Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
| Sequence Similarities | Belongs to the protein kinase superfamily. Ser/Thr protein kinase family. Aurora subfamily. |
| Name | Aurka |
|---|---|
| Function | Mitotic serine/threonine kinase that contributes to the regulation of cell cycle progression (By similarity). Associates with the centrosome and the spindle microtubules during mitosis and plays a critical role in various mitotic events including the establishment of mitotic spindle, centrosome duplication, centrosome separation as well as maturation, chromosomal alignment, spindle assembly checkpoint, and cytokinesis (PubMed:9245792, PubMed:19075002). Required for normal spindle positioning during mitosis and for the localization of NUMA1 and DCTN1 to the cell cortex during metaphase (By similarity). Required for initial activation of CDK1 at centrosomes (By similarity). Phosphorylates numerous target proteins, including ARHGEF2, BORA, BRCA1, CDC25B, DLGP5, HDAC6, KIF2A, LATS2, NDEL1, PARD3, PPP1R2, PLK1, RASSF1, TACC3, p53/TP53 and TPX2 (By similarity). Regulates KIF2A tubulin depolymerase activity (By similarity). Required for normal axon formation (By similarity). Plays a role in microtubule remodeling during neurite extension (PubMed:19668197). Important for microtubule formation and/or stabilization (By similarity). Also acts as a key regulatory component of the p53/TP53 pathway, and particularly the checkpoint-response pathways critical for oncogenic transformation of cells, by phosphorylating and destabilizing p53/TP53 (By similarity). Phosphorylates its own inhibitors, the protein phosphatase type 1 (PP1) isoforms, to inhibit their activity (By similarity). Inhibits cilia outgrowth (By similarity). Required for cilia disassembly via phosphorylation of HDAC6 and subsequent deacetylation of alpha-tubulin (PubMed:20643351). Regulates protein levels of the anti-apoptosis protein BIRC5 by suppressing the expression of the SCF(FBXL7) E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase substrate adapter FBXL7 through the phosphorylation of the transcription factor FOXP1 (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, spindle pole. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, microtubule organizing center, centrosome, centriole. Cell projection, neuron projection. Cell projection, cilium {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O14965}. Cytoplasm, cytoskeleton, cilium basal body. Basolateral cell membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:F1PNY0}. Note=Localizes on centrosomes in interphase cells and at each spindle pole in mitosis (PubMed:9245792) Associates with both the pericentriolar material (PCM) and centrioles (By similarity). Colocalized with SIRT2 at centrosome (By similarity) Detected at the neurite hillock in developing neurons (PubMed:19668197). The localization to the spindle poles is regulated by AAAS (By similarity). {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:O14965, ECO:0000269|PubMed:19668197, ECO:0000269|PubMed:9245792} |
| Tissue Location | Detected in embryonic neurons in dorsal root ganglia and brain cortex (at protein level). Highly expressed in testis, in about one third of the seminiferous tubules. Expression is restricted to specific spermatocytes nearing completion of prophase, with levels falling off on transition to elongated spermatids. Highly expressed in the ovary, expression in the oocyte starts around the transition to large growing follicle. Abundant expression is seen in the proliferating granulosa and thecal cells of the growing follicle, and in the young corpus luteum. Very weakly expressed in spleen and intestine. |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
AURKA(aurora kinase A), also called ARK1, AurA, AIK , AURORA2 ,BTAK, PPP1R47, STK7, STK15,STK6, is a mitotic centrosomal protein kinase. The main role of AURKA in tumor development is in controlling chromosome segregation during mitosis. Aurora A is a member of a family of mitotic serine/threonine kinases. Cell cycle and Northern blot analyses showed that peak expression of AURKA occurs during the G2/M phase and then decreases. By fluorescence in situ hybridization, AURKA gene is represented by 2 signals in chromosome bands 20q13.2-q13.3 and 1q41-q42. The AURKA gene is overexpressed in many human cancers. Ectopic overexpression of Aurora kinase A in mammalian cells induces centrosome amplification, chromosome instability, and oncogenic transformation, a phenotype characteristic of loss-of-function mutations of p53. Depletion of Ajuba prevented activation of AURKA at centrosomes in late G2 phase and inhibited mitotic entry. Activation of AURKA was independently sufficient to induce rapid ciliary resorption, and AURKA acted in this process through phosphorylation of HDAC6, leading to HDAC6-dependent tubulin deacetylation and destabilization of the ciliary axoneme. Small molecule inhibitors of AURKA and HDAC6 reduced regulated disassembly of cilia.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.




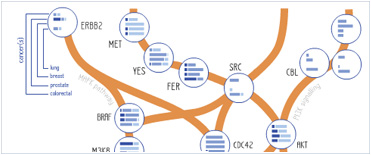







 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.


