Goat Anti-PARP2 Antibody
Peptide-affinity purified goat antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB, E |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | Q9UGN5 |
| Other Accession | NP_005475, 10038 |
| Reactivity | Human |
| Host | Goat |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Concentration | 100ug/200ul |
| Isotype | IgG |
| Calculated MW | 66206 Da |
| Gene ID | 10038 |
|---|---|
| Other Names | Poly [ADP-ribose] polymerase 2, PARP-2, hPARP-2, 2.4.2.30, ADP-ribosyltransferase diphtheria toxin-like 2, ARTD2, NAD(+) ADP-ribosyltransferase 2, ADPRT-2, Poly[ADP-ribose] synthase 2, pADPRT-2, PARP2, ADPRT2, ADPRTL2 |
| Format | 0.5 mg IgG/ml in Tris saline (20mM Tris pH7.3, 150mM NaCl), 0.02% sodium azide, with 0.5% bovine serum albumin |
| Storage | Maintain refrigerated at 2-8°C for up to 6 months. For long term storage store at -20°C in small aliquots to prevent freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | Goat Anti-PARP2 Antibody is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | PARP2 {ECO:0000303|PubMed:20092359, ECO:0000312|HGNC:HGNC:272} |
|---|---|
| Function | Poly-ADP-ribosyltransferase that mediates poly-ADP- ribosylation of proteins and plays a key role in DNA repair (PubMed:10364231, PubMed:25043379, PubMed:27471034, PubMed:30104678, PubMed:32028527, PubMed:32939087, PubMed:34486521, PubMed:34874266, PubMed:34108479). Mediates glutamate, aspartate or serine ADP- ribosylation of proteins: the ADP-D-ribosyl group of NAD(+) is transferred to the acceptor carboxyl group of target residues and further ADP-ribosyl groups are transferred to the 2'-position of the terminal adenosine moiety, building up a polymer with an average chain length of 20-30 units (PubMed:25043379, PubMed:30104678, PubMed:30321391). Serine ADP-ribosylation of proteins constitutes the primary form of ADP-ribosylation of proteins in response to DNA damage (PubMed:32939087). Mediates glutamate and aspartate ADP-ribosylation of target proteins in absence of HPF1 (PubMed:25043379). Following interaction with HPF1, catalyzes serine ADP-ribosylation of target proteins; HPF1 conferring serine specificity by completing the PARP2 active site (PubMed:28190768, PubMed:32028527, PubMed:34486521, PubMed:34874266, PubMed:34108479). PARP2 initiates the repair of double-strand DNA breaks: recognizes and binds DNA breaks within chromatin and recruits HPF1, licensing serine ADP-ribosylation of target proteins, such as histones, thereby promoting decompaction of chromatin and the recruitment of repair factors leading to the reparation of DNA strand breaks (PubMed:10364231, PubMed:32939087, PubMed:34108479). HPF1 initiates serine ADP-ribosylation but restricts the polymerase activity of PARP2 in order to limit the length of poly- ADP-ribose chains (PubMed:34732825, PubMed:34795260). Specifically mediates formation of branched poly-ADP-ribosylation (PubMed:30104678). Branched poly-ADP-ribose chains are specifically recognized by some factors, such as APLF (PubMed:30104678). In addition to proteins, also able to ADP-ribosylate DNA: preferentially acts on 5'-terminal phosphates at DNA strand breaks termini in nicked duplex (PubMed:27471034, PubMed:29361132). |
| Cellular Location | Nucleus. Chromosome. Note=Recruited to DNA damage sites in a PARP1-dependent process: recognizes and binds poly-ADP-ribose chains produced by PARP1 at DNA damage sites via its N-terminus, leading to its recruitment. |
| Tissue Location | Widely expressed, mainly in actively dividing tissues (PubMed:10364231). The highest levels are in the brain, heart, pancreas, skeletal muscle and testis; also detected in kidney, liver, lung, placenta, ovary and spleen; levels are low in leukocytes, colon, small intestine, prostate and thymus (PubMed:10364231) |

Thousands of laboratories across the world have published research that depended on the performance of antibodies from Abcepta to advance their research. Check out links to articles that cite our products in major peer-reviewed journals, organized by research category.
info@abcepta.com, and receive a free "I Love Antibodies" mug.
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
This gene encodes poly(ADP-ribosyl)transferase-like 2 protein, which contains a catalytic domain and is capable of catalyzing a poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation reaction. This protein has a catalytic domain which is homologous to that of poly (ADP-ribosyl) transferase, but lacks an N-terminal DNA binding domain which activates the C-terminal catalytic domain of poly (ADP-ribosyl) transferase. The basic residues within the N-terminal region of this protein may bear potential DNA-binding properties, and may be involved in the nuclear and/or nucleolar targeting of the protein. Two alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been found.
References
Variation at the NFATC2 Locus Increases the Risk of Thiazolinedinedione-Induced Edema in the Diabetes REduction Assessment with ramipril and rosiglitazone Medication (DREAM) Study. Bailey SD, et al. Diabetes Care, 2010 Jul 13. PMID 20628086.
Variation within DNA repair pathway genes and risk of multiple sclerosis. Briggs FB, et al. Am J Epidemiol, 2010 Jul 15. PMID 20522537.
Crystal structure of the catalytic domain of human PARP2 in complex with PARP inhibitor ABT-888. Karlberg T, et al. Biochemistry, 2010 Feb 16. PMID 20092359.
Gene-centric association signals for lipids and apolipoproteins identified via the HumanCVD BeadChip. Talmud PJ, et al. Am J Hum Genet, 2009 Nov. PMID 19913121.
LMTK2 and PARP-2 gene polymorphism and azoospermia secondary to meiotic arrest. Sakugawa N, et al. J Assist Reprod Genet, 2009 Sep-Oct. PMID 19806447.
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.




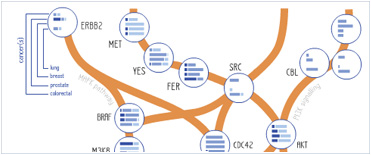







 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.


