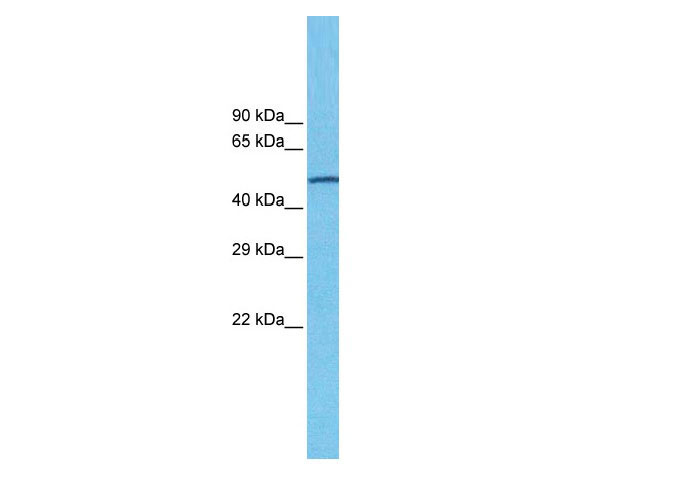
CHRNA7 antibody - N-terminal region
Rabbit Polyclonal Antibody
- SPECIFICATION
- CITATIONS
- PROTOCOLS
- BACKGROUND

Application
| WB |
|---|---|
| Primary Accession | P36544 |
| Other Accession | NM_000746, NP_000737 |
| Reactivity | Human, Mouse, Rat, Bovine |
| Predicted | Human, Mouse, Rat, Chicken, Bovine |
| Host | Rabbit |
| Clonality | Polyclonal |
| Calculated MW | 56kDa |
| Gene ID | 1139;89832 |
|---|---|
| Alias Symbol | NACHRA7, CHRNA7-2 |
| Other Names | Neuronal acetylcholine receptor subunit alpha-7, CHRNA7, NACHRA7 |
| Format | Liquid. Purified antibody supplied in 1x PBS buffer with 0.09% (w/v) sodium azide and 2% sucrose. |
| Reconstitution & Storage | Add 100 ul of distilled water. Final anti-CHRNA7 antibody concentration is 1 mg/ml in PBS buffer with 2% sucrose. For longer periods of storage, store at 20°C. Avoid repeat freeze-thaw cycles. |
| Precautions | CHRNA7 antibody - N-terminal region is for research use only and not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. |
| Name | CHRNA7 (HGNC:1960) |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | NACHRA7 |
| Function | Component of neuronal acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) that function as pentameric, ligand-gated cation channels with high calcium permeability among other activities. nAChRs are excitatory neurotrasnmitter receptors formed by a collection of nAChR subunits known to mediate synaptic transmission in the nervous system and the neuromuscular junction. Each nAchR subunit confers differential attributes to channel properties, including activation, deactivation and desensitization kinetics, pH sensitivity, cation permeability, and binding to allosteric modulators (PubMed:15609996, PubMed:33735609, PubMed:8145738). CHRNA7 forms homopentameric neuronal acetylcholine receptors abundantly expressed in the central nervous system, characterized by fast desensitization and high calcium permeability (PubMed:31560909, PubMed:33735609, PubMed:38382524, PubMed:8145738). Also forms heteropentamers with CHRNB2, mainly expressed in basal forebrain cholinergic neurons. Involved in the modulation of calcium- dependent signaling pathways and influences the release of neurotransmitters, including dopamine, glutamate and GABA (PubMed:33239400). Also expressed in non-neuronal cells such as immune cells like lymphocytes, monocytes and macrophages (PubMed:12508119, PubMed:16968406, PubMed:25259522). In T cells, activation induces metabotropic signaling that results in an increase of intracellular Ca2+ concentrations, independent of ionotropic receptor functions (PubMed:17709503). In macrophages, required for acetylcholine-mediated inhibition of TNF and other inflammatory cytokine release (PubMed:12508119). Once activated by acetylcholine, nicotine or other agonists, selectively inhibits production of pro-inflammatory cytokines while leaving anti-inflammatory cytokines undisturbed (PubMed:12508119, PubMed:25259522). Stimulates the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway, controlling inflammation by inhibiting NFKB nuclear translocation and activating the JAK2-STAT3 pathway, independently of ion channel activity (PubMed:16968406, PubMed:25259522). Also expressed in the urothelium where it modulates reflex bladder activity by increasing intracellular calcium through internal stores and decreasing basal ATP release (By similarity). |
| Cellular Location | Postsynaptic cell membrane {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q05941}; Multi-pass membrane protein. Cell membrane; Multi-pass membrane protein. Note=TMEM35A/NACHO promotes its trafficking to the cell membrane (PubMed:27789755). RIC3 promotes its trafficking to the cell membrane (By similarity) {ECO:0000250|UniProtKB:Q05941, ECO:0000269|PubMed:27789755} |
| Tissue Location | Expressed in neuronal cells (PubMed:8145738). Expressed in macrophages (at protein level) (PubMed:12508119) |
If you have used an Abcepta product and would like to share how it has performed, please click on the "Submit Review" button and provide the requested information. Our staff will examine and post your review and contact you if needed.
If you have any additional inquiries please email technical services at tech@abcepta.com.












 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.