Application Protocols
Provided below are standard protocols that you may find useful for product applications.
Background
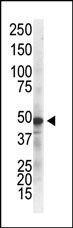
This gene encodes the regulatory subunit of the inhibitor of kappaB kinase (IKK) complex, which activates NF-kappaB resulting in activation of genes involved in inflammation, immunity, cell survival, and other pathways. Mutations in this gene result in incontinentia pigmenti, hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia, and several other types of immunodeficiencies. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. A pseudogene highly similar to this locus is located in an adjacent region of the X chromosome.
References
Immune deficiency caused by impaired expression of nuclear factor-kappaB essential modifier (NEMO) because of a mutation in the 5' untranslated region of the NEMO gene. Mooster JL, et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2010 Jul. PMID 20542322.
NEMO gene mutations in Chinese patients with incontinentia pigmenti. Hsiao PF, et al. J Formos Med Assoc, 2010 Mar. PMID 20434027.
The LCR at the IKBKG locus is prone to recombine. Fusco F, et al. Am J Hum Genet, 2010 Apr 9. PMID 20380930.
IKK{gamma} protein is a target of BAG3 regulatory activity in human tumor growth. Ammirante M, et al. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2010 Apr 20. PMID 20368414.
Activation of noncanonical NF-kappaB signaling by the oncoprotein Tio. de Jong SJ, et al. J Biol Chem, 2010 May 28. PMID 20353939.






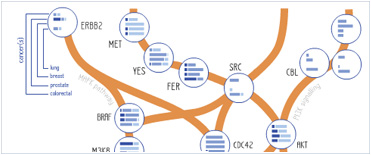







 Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them.
Foundational characteristics of cancer include proliferation, angiogenesis, migration, evasion of apoptosis, and cellular immortality. Find key markers for these cellular processes and antibodies to detect them. The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle.
The SUMOplot™ Analysis Program predicts and scores sumoylation sites in your protein. SUMOylation is a post-translational modification involved in various cellular processes, such as nuclear-cytosolic transport, transcriptional regulation, apoptosis, protein stability, response to stress, and progression through the cell cycle. The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.
The Autophagy Receptor Motif Plotter predicts and scores autophagy receptor binding sites in your protein. Identifying proteins connected to this pathway is critical to understanding the role of autophagy in physiological as well as pathological processes such as development, differentiation, neurodegenerative diseases, stress, infection, and cancer.